ACE Inhibitors: Mechanism of Action and Uses
ACE Inhibitors FAQ
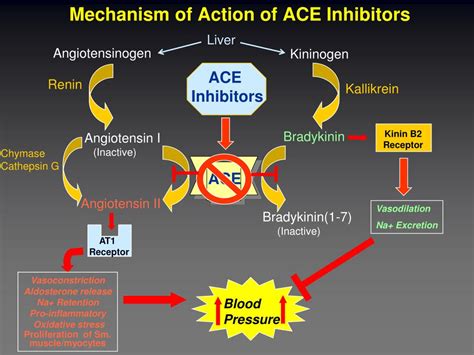
How do ACE inhibitors work?
By inhibiting the production of Angiotensin II, ACE inhibitors keep the blood vessels open. This reduces blood pressure and lowers the risk of complications associated with hypertension. Most people take ACE inhibitors orally, but some may administer the drug intravenously.
What are angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors?
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors are medicines that help relax the veins and arteries to lower blood pressure. ACE inhibitors prevent an enzyme in the body from making angiotensin 2, a substance that narrows blood vessels. This narrowing can cause high blood pressure and forces the heart to work harder.
What are the side effects of an ACE inhibitor?
Like any drug, an ACE inhibitor is likely to have some side effects. They may include: Cough. If this symptom persists or is severe, contact your doctor. Ask your doctor what type of cough medicine you should use to control the cough. Your doctor may switch you to a different medication that will not cause a cough, Red, itchy skin or rash.
What are some examples of ACE inhibitors?
Examples of ACE inhibitors include benazepril (Lotensin), captopril (Capoten), enalapril (Vasotec), fosinopril (Monopril), and ramipril (Altace). Examples of the most common side effects of this class of drugs are dizziness, headache, cough, rash, chest pain, and rash.
What are ACE inhibitors used for?
These medicines are commonly used to treat high blood pressure, heart problems and more. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors are medicines that help relax the veins and arteries to lower blood pressure. ACE inhibitors prevent an enzyme in the body from making angiotensin 2, a substance that narrows blood vessels.
Are ACE inhibitors a primary etiology?
Amandeep Goyal; Austin S. Cusick; Blair Thielemier. Last Update: June 26, 2023. ACE inhibitors are a medication class used to treat and manage hypertension, a significant risk factor for coronary disease, heart failure, stroke, and a number of other cardiovascular conditions. Most cases are primary and not attributable to any specific etiology.
Do ACE inhibitors reduce blood pressure?
In high blood pressure (hypertension), ACE inhibitors should help to reduce the blood pressure. In heart failure, there may be too much circulating fluid in the blood vessels. ACE inhibitors help to reduce this. They appear to have a protective effect on the heart and slow the progression of the heart failure. Who cannot take ACE inhibitors?
ACE Inhibitors References
If you want to know more about ACE Inhibitors, consider exploring links below:
What Is ACE Inhibitors
- https://www.drugs.com/drug-class/angiotensin-converting-enzyme-inhibitors.html
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/in-depth/ace-inhibitors/art-20047480
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326791
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ACE_inhibitor
- https://www.medicinenet.com/ace_inhibitors/article.htm
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/21934-ace-inhibitors
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK431051/
- https://www.healthline.com/health/heart-disease/ACE-inhibitors
- https://patient.info/heart-health/ace-inhibitors
- https://www.webmd.com/hypertension-high-blood-pressure/treatment-ace-inhibitors
ACE Inhibitors Information
Explore Related Topics
What are the common drug interactions with antibiotics?
Participants can share and learn about common drug interactions that may occur when taking antibiotics alongside other medications in this informative thread.