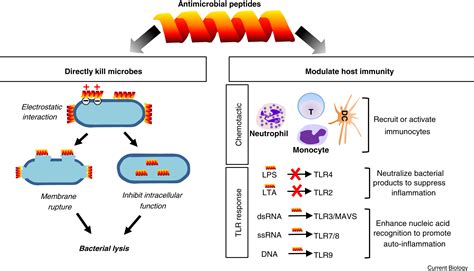
Antimicrobial Peptides - Nature's Defense Against Pathogens
Antimicrobial Peptides FAQ
What are antimicrobial peptides (AMPs)?
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are endogenous polypeptides produced by multicellular organisms in order to protect a host from pathogenic microbes.
What are antimicrobial peptides?
Antimicrobial peptides can be obtained from microorganisms like bacteria and fungi, and some famous peptides are nisin, gramicidin from Lactococcus lactis, Bacillus subtilis, and Bacillus brevis ( Cao et al., 2018 ). Due to the high price of chemical synthesis of AMPs, the biological expression has attracted the increase of attention.
Are antimicrobial peptides a solution to the antibiotic-resistance crisis?
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are a diverse class of molecules that represent a vital part of innate immunity. AMPs are evolutionarily conserved molecules that exhibit structural and functional diversity. They provide a possible solution to the antibiotic-resistance crisis.
Are antimicrobial peptides resistant to antibiotics?
In vitro studies found that synergies are frequent and that other traits of AMPs result in a low probability of resistance evolution compared with conventional antibiotics. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are essential components of immune defenses of multicellular organisms and are currently in development as anti-infective drugs.
How many antimicrobial peptides are there?
A total of 3,240 AMPs have been reported in the antimicrobial peptide database (APD3 1) updated on August 24, 2020. Different types of AMPs have the following commonalities: their number of amino acid residues is between 10 and 60 (average: 33.26), and almost all AMPS are cationic (average net charge: 3.32).
Antimicrobial Peptides References
If you want to know more about Antimicrobial Peptides, consider exploring links below:
What Is Antimicrobial Peptides
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7596191/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antimicrobial_peptides
- https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/microbiology/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2020.582779/full
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41573-019-0058-8
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11033-022-07572-1
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.aau5480
Explore Related Topics
How can we address antibiotic resistance in livestock and agriculture?
Examine the role of antibiotics in livestock farming and agriculture, and their contribution to the spread of antibiotic resistance. What measures can be taken to minimize the use of antibiotics in animal agriculture and prevent the transmission of resistant bacteria to humans? Share your insights on addressing antibiotic resistance in the livestock and agriculture sectors.