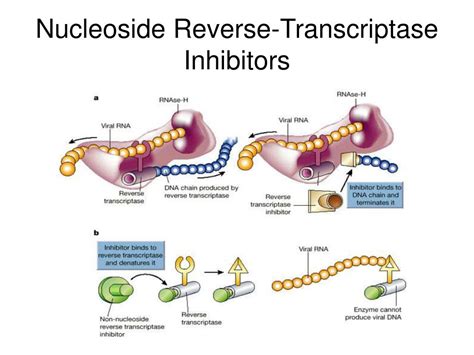
Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors: Mechanism of Action
Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors FAQ
What are nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors?
The nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) were the first class of antiretroviral drugs to be approved by the FDA. NRTIs are taken as prodrugs and must be taken into the host cell and phosphorylated before they become active. Once inside the host cell, cellular kinases will activate the drug.
Are nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors effective in limiting HIV-1 infection?
Among various Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved ARVs, nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) are most effective in limiting HIV-1 infection. This review focuses on NRTIs mechanism of action and metabolism. A search of PubMed (1982–2016) was performed to capture relevant articles regarding NRTI pharmacology.
What is a reverse transcriptase inhibitor (RTI)?
Reverse-transcriptase inhibitors ( RTIs) are a class of antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV infection or AIDS, and in some cases hepatitis B. RTIs inhibit activity of reverse transcriptase, a viral DNA polymerase that is required for replication of HIV and other retroviruses .
Are reverse transcriptase inhibitors effective against HIV?
Reverse transcriptase inhibitors are active against HIV, a retrovirus. The drugs inhibit RNA virus replication by reversible inhibition of viral HIV reverse transcriptase, which reverse transcribes viral RNA into DNA for insertion into the host DNA sequence (see Fig. 51.6 ).
What is a reverse transcriptase inhibitor?
Parth H. Patel; Hassam Zulfiqar. Last Update: June 25, 2023. Reverse transcriptase inhibitors are medications used in the management and treatment of HIV. It is in the antiretroviral class of drugs. This activity reviews the indication, action, and contraindications for RTIs as a valuable agent in managing HIV (and other disorders when applicable).
Do HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors phosphorylate DNA?
They inhibit the HIV reverse transcriptase enzyme competitively and terminate synthesis of DNA chains. Nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (nRTIs) competitively inhibit the HIV reverse transcriptase enzyme, as do NRTIs, but do not require initial phosphorylation.
Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors References
If you want to know more about Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors, consider exploring links below:
What Is Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551504/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reverse-transcriptase_inhibitor
- https://www.healthline.com/health/hiv-aids/nucleoside-nucleotide-reverse-transcriptase-inhibitors
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/nrtis
- https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Microbiology/Microbiology_(Boundless)/13%3A_Antimicrobial_Drugs/13.07%3A_Antiviral_Drugs/13.7C%3A_Nucleotide_and_Nonnucleotide_Reverse_Transcriptase_Inhibitors
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/reverse-transcriptase-inhibitors
- https://clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/en/guidelines/hiv-clinical-guidelines-adult-and-adolescent-arv/nucleoside-reverse-transcriptase