Applications of Phage-derived Enzymes in Biotechnology
Phage-derived Enzymes FAQ
What are phage derived enzymes?
Two classes of phage-derived enzymes are commonly described: peptidoglycan hydrolases (also referred to as “lysins”), which degrade the bacterial cell wall, and polysaccharide depolymerases, which break down bacterial surface-associated polysaccharides.
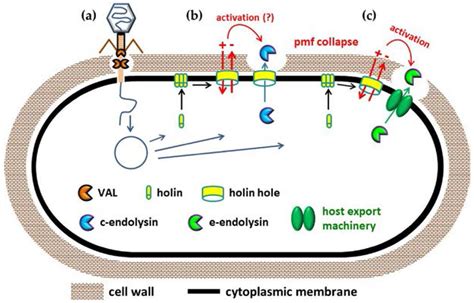
Are phage encoded endolysins depolymerases?
The term depolymerase can refer to any generic protein that is able to degrade polymers. From this perspective, phage encoded endolysins are also depolymerases, since they cleave the peptidoglycan, a bacterial polysaccharide in general in an hydrolase manner ( Schmelcher and Loessner, 2016 ).
Should phages be used as antibacterial agents?
Phage therapy skepticism. A somewhat unique challenge to the use of phages as antibacterial agents is a combination of their long history and insufficiently well-documented efficacy. The former allowed for the initial “enthusiasm” for phage use.
What are phage integrases and recombinases?
Phage integrases and recombinases catalyse the site-specific recombination of two sequences ( att sites), and many, including those from phage Bxb1 and phage ΦC31, have been exploited in synthetic biology and other applications to drive integration, excision and inversion events 76.
What are phage lytic enzymes?
Viruses. 2019 Feb; 11 (2): 113. Phage lytic enzymes are enzymes produced by bacterial viruses, either as part of their virion to facilitate bacterial infection through local peptidoglycan degradation, or as soluble proteins to induce massive cell lysis at the end of the lytic replication cycle.
Are phage enzymes effective in promoting bacterial envelope degradation?
Encouraging performances were noted especially for phage enzymes involved in the first step of viral infection responsible for bacterial envelope degradation, named depolymerases.
What are phage-encoded proteins used for?
The main promises are associated with phage and phage-encoded proteins utilization in: (i) phage typing; (ii) phage therapy; (iii) food decontamination; (iv) medical devices disinfection; (v) bacterial detection; (vi) drug delivery (vehicles) and (vii) molecular biology.
What are phage-associated enzymes?
Depending on the mode of degradation of carbohydrate-containing polymers on the surface of bacterial cells, phage-associated enzymes fall into two main groups: hydrolases (EC 3.2.1.-) and lyases (EC 4.2.2.-) [ 68 ]. The first ones degrade either the peptidoglycan, capsular polysaccharides or the O-antigen side-chains of LPS.
Phage-derived Enzymes References
If you want to know more about Phage-derived Enzymes, consider exploring links below:
What Is Phage-derived Enzymes
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1198743X23005281
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6966330/
- https://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002119
- https://www.nature.com/articles/nrmicro3564
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29844287/
Phage-derived Enzymes Information
Explore Related Topics
Are there new technologies being developed to tackle antibiotic resistance?
Explore cutting-edge technologies and innovations aimed at combating antibiotic resistance and developing novel treatment options.