Innovative Therapies for Resistant Infections
Resistant Infection Treatments FAQ
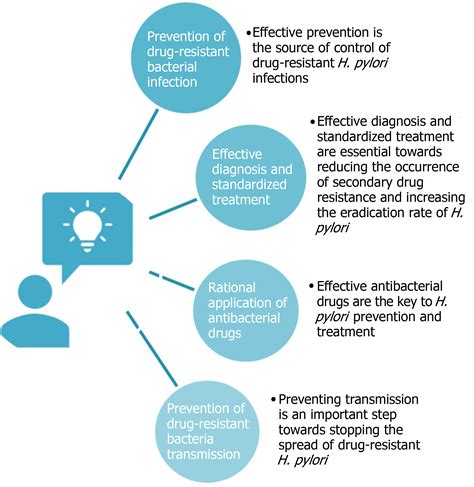
What is antimicrobial resistance?
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when some of the germs (bacteria, virus, or fungus) that cause infections resist the effects of the medicines used to treat them. This may lead to ‘treatment failure’, or the inability to treat the cause of the infection. The types of microorganisms that can develop resistance to antimicrobials include:
How can we prevent antibiotic resistance?
Practice good hygiene. Protecting yourself from infection can help you avoid bacterial infections that need antibiotics. The more we use antibiotics as a society, the more the problem of antibiotic resistance can grow. Handwashing is one important step you can take.
What is antibiotic resistance & why is it important?
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when germs (bacteria, virus, or fungus) that cause infections resist the effects of the medicines used to treat them. These resistant bacteria can spread and may infect people or animals. They are harder to treat than non-resistant bacteria. Why are antibiotics important? What is antibiotic resistance?
How do you deal with antimicrobial resistant bacteria?
Antimicrobial resistant bacteria can also be passed from person to person within the community. This is becoming more common. Wash hands before and after food handling, after going to the toilet and changing nappies. Cover your nose and mouth when coughing and sneezing. Use tissues to blow or wipe your nose.
How can antibiotic resistance be prevented?
The development of antibiotic resistance can be prevented by minimising unnecessary prescribing and overprescribing of antibiotics, the correct use of prescribed antibiotics, and good hygiene and infection control practices. Some bacteria have developed resistance to antibiotics that were once commonly used to treat them.
What is antibiotic resistance?
Antibiotic resistance is when bacteria change to resist antibiotics that used to effectively treat them. This makes certain bacterial infections difficult to treat. Overuse and misuse of antibiotics cause antibiotic resistance. You can help combat this global health problem by taking these drugs only when your provider says they’re necessary.
Resistant Infection Treatments References
If you want to know more about Resistant Infection Treatments, consider exploring links below:
What Is Resistant Infection Treatments
- https://www.amr.gov.au/about-amr/what-amr
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/21655-antibiotic-resistance
- https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/staph-infections
- https://wellcome.org/news/what-are-drug-resistant-infections
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7047908/
- https://www.safetyandquality.gov.au/publications-and-resources/resource-library/amr-what-antimicrobial-resistance-and-how-can-we-fight-it-media-backgrounder
- https://www.niaid.nih.gov/research/antimicrobial-resistance-treatment
Resistant Infection Treatments Information
Explore Related Topics
Telemedicine consultations for resistant infections: Are they the future of healthcare?
Debate whether telemedicine consultations are the future of healthcare for managing resistant infections and share your perspectives on this innovative approach.