Understanding Enzyme Cofactors in Biochemistry
Enzyme Cofactors FAQ
Does enzyme have a cofactor?
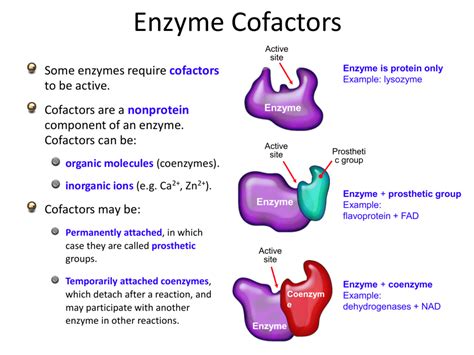
This action is not available. Many enzymes are simple proteins consisting entirely of one or more amino acid chains. Other enzymes contain a nonprotein component called a cofactor that is necessary for the enzyme’s proper functioning. This cofactor is usually weakly bonded to the polypeptide chains through intermolecular interactions.
What is the difference between cofactor and coenzyme?
The cofactor is primarily a metal associated with the enzyme’s catalytic properties. On the other hand, a coenzyme is an organic substance that usually serves as a donor or acceptor of atoms added to or removed from the substrate. Define an enzyme. A macromolecule that catalyses a chemical process is known as an enzyme.
What are cofactors and holoenzymes?
These are known as cofactors, and without these enzymes remain within the inactive “apoenzyme” forms. Once the cofactor is added, the enzyme becomes the active “holoenzyme”. Cofactors can either be ions, such as zinc and iron ions, or organic molecules, such as vitamins or vitamin-derived molecules.
What is a cofactor in biology?
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical that assists with a biological chemical reaction. Co-factors may be metal ions, organic compounds, or other chemicals that have helpful properties not usually found in amino acids. Some cofactors can be made inside the body, such as ATP, while others must be consumed in food.
Why do enzymes need a cofactor?
They can assist the enzyme in carrying out some essential processes that it cannot carry out on its own. A cofactor is a chemical or metallic ion that is not a protein and is necessary for the catalytic function of an enzyme (a catalyst increases the rate of a chemical reaction).
What are the three groups of enzyme cofactors?
Heme groups (the orange, lavender, and grey) participate in enzyme activity (for example, a human cytochrome) In this article, we explore mechanics and importance the three main groups of enzyme cofactors: metal ions, cosubstrates, and prosthetic groups.
What are cofactors & coenzymes?
The cofactors and coenzymes (organic cofactors) that help enzymes catalyze reactions. Want to join the conversation? why such a big and complex protein to transform so little a substrate....
Enzyme Cofactors References
If you want to know more about Enzyme Cofactors, consider exploring links below:
What Is Enzyme Cofactors
- https://byjus.com/biology/enzyme-cofactors/
- https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Brevard_College/CHE_301_Biochemistry/05%3A_Enzymes/5.02%3A_Enzyme_Cofactors
- https://www.news-medical.net/life-sciences/What-is-an-Enzyme-Cofactor.aspx
- https://biologydictionary.net/cofactor/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cofactor_(biochemistry)
- https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/energy-and-enzymes/enzyme-regulation/v/enzyme-cofactors-and-coenzymes
- https://chemistrytalk.org/enzyme-cofactors/
- https://www.britannica.com/science/cofactor
Enzyme Cofactors Information
Explore Related Topics
Are there effective alternatives to antibiotics that could help combat resistance?
Explore innovative approaches and alternative treatments that could help address antibiotic resistance and reduce reliance on traditional antibiotics. From phage therapy to probiotics, what emerging solutions show promise in combating resistant bacteria and infections? Share your views on potential alternatives to antibiotics in the era of increasing resistance.