Type 2 Diabetes - Causes and Management
Type 2 Diabetes FAQ
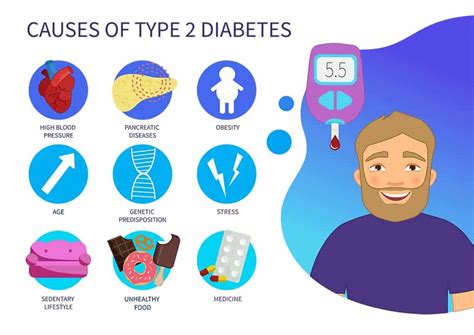
What are the risk factors for type 2 diabetes?
Viral infections and environmental triggers may contribute to its onset. Type 2 Diabetes: Risk factors include a family history of diabetes, obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, and age. Ethnicity, gestational diabetes, and certain medical conditions also elevate the risk.
What are the consequences of type 2 diabetes?
There are several consequences of type 2 diabetes which contribute to an impaired way in which sugar (glucose) is used in the body to fuel it. By having this chronic condition for a long period, too much sugar enters the body. In the long run, excessive blood sugar can cause circulatory, nervous, and immune system problems.
How can type 2 diabetes be prevented?
Type 2 Diabetes: Prevention is possible through lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management. Early detection and intervention in individuals at risk can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes. 7. Complications:
What is type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a condition in which the body becomes resistant to the normal effects of insulin and gradually loses the capacity to produce enough insulin in the pancreas. The condition has strong genetic and family-related (non-modifiable) risk factors and is also often associated with modifiable lifestyle risk factors.
What does a type 2 diabetes diagnosis mean?
A type 2 diabetes diagnosis means your pancreas is not working as effectively as it needs to. Your body is building insulin resistance and is unable to effectively convert glucose into energy, leaving too much glucose in your blood. The good news? There’s something you can do today to look after your health.
What are the symptoms of type 2 diabetes?
Symptoms of diabetes may occur suddenly. In type 2 diabetes, the symptoms can be mild and may take many years to be noticed. Over time, diabetes can damage blood vessels in the heart, eyes, kidneys and nerves. People with diabetes have a higher risk of health problems including heart attack, stroke and kidney failure.
Type 2 Diabetes References
If you want to know more about Type 2 Diabetes, consider exploring links below:
What Is Type 2 Diabetes
- https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/type-2-diabetes
- https://www.diabetesaustralia.com.au/about-diabetes/type-2-diabetes/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/type-2-diabetes/symptoms-causes/syc-20351193
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21501-type-2-diabetes
- https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/diabetes/diabetes/contents/how-common-is-diabetes/type-2-diabetes
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes/type-2-diabetes
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes
- https://diabetes.org/about-diabetes/type-2
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Type_2_diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes Information
Explore Related Topics
How can antibiotics interact with diabetes medications?
Delve into the topic of antibiotic interactions with diabetes medications, discussing the precautions and considerations for individuals managing both conditions simultaneously.
What are the common drug interactions with antibiotics?
Participants can share and learn about common drug interactions that may occur when taking antibiotics alongside other medications in this informative thread.