Immunomodulators: Mechanism of Action
Immunomodulators FAQ
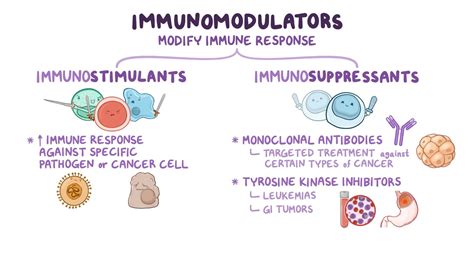
What are immunomodulating agents?
Immune-modulating agents are a type of immunotherapy that enhance the body’s immune response against cancer. They can also help with certain side effects caused by other cancer treatments.
What is immunomodulation in Physiology?
Immunomodulation, the process by which the immune responses are induced, amplified, or attenuated. A great number of agents that can modulate pathophysiological processes are known to be immunomodulators [ 4 ]. Immune modulators of synthetic or biological origin modulate, suppress and stimulate any components of adaptive or innate immunity [ 5 ].
What is a non-specific-action immunomodulator?
Non-specific-action immunomodulators are used to stimulate or suppress the immune response, without directing the activity of stimulated cells to a specific antigen.
What are immunomodulatory therapies?
Immunomodulatory therapies mainly focus on activating, modulating, and regulating the host immune system's function, as modulation may promote resistance and finally arrest infections. Recently, clinical studies have used adjunct therapies with recombinant forms of natural immunomodulators to aid antivirals and antibiotics [ 128 ].
Immunomodulators References
If you want to know more about Immunomodulators, consider exploring links below:
What Is Immunomodulators
- https://www.healthline.com/health/immunomodulators
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/drugs/24987-immunomodulators
- https://www.rxlist.com/how_do_immunomodulators_work/drug-class.htm