Polymyxins - Antibiotics for Multidrug-resistant Infections
Polymyxins FAQ
What are polymyxins used for?
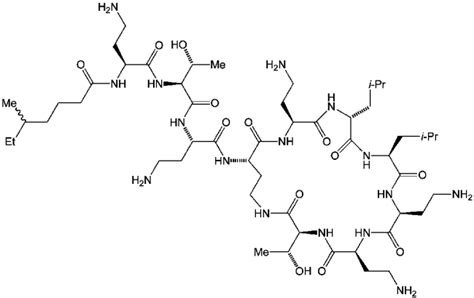
Polymyxins comprise a class of antibiotics targeting gram-negative bacterial infections. Polymyxin B and Polymyxin E (colistin) are the two drugs within this antibiotic class used primarily in clinical practice.
Are polymyxins antibiotics?
Polymyxins are antibiotics. Polymyxins B and E (also known as colistin) are used in the treatment of Gram-negative bacterial infections. They work mostly by breaking up the bacterial cell membrane. They are part of a broader class of molecules called nonribosomal peptides .
What are Polymyxins B & E?
Polymyxins B and E (also known as colistin) are used in the treatment of Gram-negative bacterial infections. They work mostly by breaking up the bacterial cell membrane. They are part of a broader class of molecules called nonribosomal peptides . They are produced in nature by Gram-positive bacteria such as Paenibacillus polymyxa .
Is colistin a polymyxin?
Colistin (also known as polymyxin E) is a polypeptide antibiotic that was originally isolated in 1947 from the soil bacterium Paenibacillus polymyxa subsp. colistinus ( 1 ). Colistin and polymyxin B belong to the class of polymyxins, which is one of the primary classes of antibiotics with activity against most Gram-negative bacteria.
Polymyxins References
If you want to know more about Polymyxins, consider exploring links below:
What Is Polymyxins
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557540/
- https://www.uptodate.com/contents/polymyxins-an-overview
- https://www.britannica.com/science/polymyxin
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/polymyxin
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32491472/
Polymyxins Information
Explore Related Topics
Are there any alternatives to Aminoglycosides for treating bacterial infections?
Share information on alternative antibiotics to Aminoglycosides for the treatment of bacterial infections and discuss their pros and cons.