The Perils of Antivirals: Protecting the Liver from Gastrointestinal Infections
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Mar-30
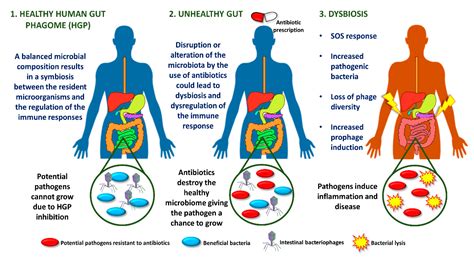
As the world continues to grapple with the ever-evolving landscape of viral infections, the use of antiviral medications has become increasingly prevalent. While these drugs can be instrumental in combating various viral illnesses, including those affecting the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, a growing body of evidence suggests that they may also carry the risk of liver damage in certain individuals.
Gastrointestinal infections, such as those caused by viruses like norovirus or rotavirus, can wreak havoc on the digestive system, leading to symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. In such cases, healthcare providers may prescribe antiviral medications to help alleviate the severity and duration of the illness. However, the potential for these drugs to adversely impact the liver has become a cause for concern.
One of the primary mechanisms by which antivirals can contribute to liver damage is through their metabolic processing. The liver is responsible for breaking down and eliminating these medications from the body, and this process can sometimes result in the production of toxic byproducts that can harm the liver itself. Individuals with pre-existing liver conditions or certain genetic factors may be more susceptible to this phenomenon, as their livers may have a diminished capacity to handle the metabolic load.
Moreover, the concomitant use of other medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or certain antibiotics, can further exacerbate the risk of liver damage in individuals with GI infections. The synergistic effects of these drug interactions can overwhelm the liver's ability to effectively process and eliminate the various compounds, leading to a buildup of potentially harmful substances.
To mitigate the risk of liver damage associated with antiviral medications, healthcare providers often recommend close monitoring of liver function tests, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), in patients with GI infections. Prompt identification of any abnormalities in these markers can allow for early intervention and potential adjustments to the treatment regimen.
Additionally, preventive measures, such as ensuring adequate hydration, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and maintaining a balanced diet, can help support the liver's overall health and resilience during the course of GI infections and antiviral treatment.
In cases where the risk of liver damage is deemed particularly high, healthcare providers may opt for alternative treatment approaches, such as the use of probiotics or herbal remedies, which have shown promise in managing certain GI infections without the same level of hepatic stress.
As the medical community continues to explore the complex interplay between antiviral medications, gastrointestinal infections, and liver health, it is crucial for patients and healthcare providers to remain vigilant and work collaboratively to ensure the safe and effective management of these conditions.
So, the question remains: can antivirals lead to liver damage in individuals with gastrointestinal infections? The answer, it seems, is a cautionary "yes" – but with proactive monitoring and a multifaceted approach to care, the risks can be mitigated, and the benefits of these essential medications can be realized while safeguarding the liver's well-being.
User comments
More Topics to Explore
How to manage diarrhea caused by antibiotics?
Discuss tips and remedies to manage diarrhea as a side effect of antibiotics in the context of gastrointestinal infections.
Are there natural remedies to counteract antibiotic-induced yeast infections?
Exchange insights on natural remedies or preventive measures to combat yeast infections resulting from antibiotic use in the treatment of gastrointestinal infections.
How common are allergic reactions to antibiotics for gastrointestinal infections?
Discuss the prevalence of allergic reactions to antibiotics used in the treatment of gastrointestinal infections and share experiences or concerns regarding allergies.
What are the long-term risks of frequent antibiotic use for gastrointestinal issues?
Delve into the potential long-term consequences of frequent antibiotic use in managing gastrointestinal infections and share perspectives on the risks involved.
How to differentiate between normal side effects and severe reactions to antibiotics for gastrointestinal issues?
Share insights on distinguishing between common side effects and severe reactions to antibiotics in the treatment of gastrointestinal problems and seek advice.
Are probiotics recommended alongside antibiotics for gastrointestinal infections?
Exchange opinions on the benefits of incorporating probiotics alongside antibiotics for gastrointestinal infections to enhance gut health and alleviate side effects.
What are the risks of antibiotic resistance when treating recurrent gastrointestinal infections?
Discuss the risks associated with antibiotic resistance in the management of recurrent gastrointestinal infections and propose strategies to prevent resistance.