Can Combining Antibiotics and Antiviral Drugs Lead to Adverse Reactions?
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Mar-21
The complex interactions between antibiotics and antiviral drugs have long been a topic of concern for healthcare professionals. As both classes of medications play vital roles in treating a wide range of infections, understanding the potential risks associated with their concomitant use is crucial for ensuring patient safety.
When antibiotics and antiviral drugs are prescribed together, the possibility of adverse reactions cannot be overlooked. These medications, while individually essential in their respective domains, can sometimes exhibit incompatibilities that can lead to undesirable outcomes. The underlying mechanisms behind these interactions are multifaceted, involving factors such as pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and metabolic pathways.
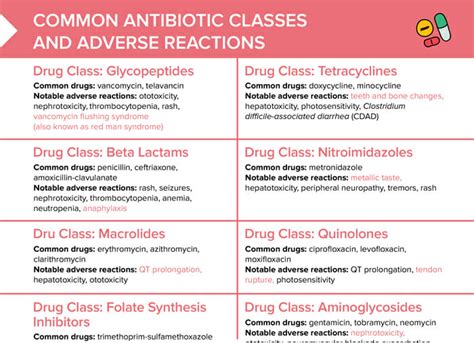
One of the primary concerns with combining antibiotics and antiviral drugs is the potential for drug-drug interactions. Certain antibiotics, such as macrolides and fluoroquinolones, are known to interact with various antiviral medications, including protease inhibitors and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. These interactions can result in altered drug concentrations, leading to either decreased efficacy or increased toxicity.
Additionally, the use of certain antibiotics, particularly broad-spectrum agents, can disrupt the delicate balance of the gut microbiome, which plays a crucial role in the body's immune response. This disturbance can potentially impact the effectiveness of antiviral therapies, as the gut microbiome is closely linked to the body's ability to fight viral infections.
Another potential concern is the risk of additive or synergistic adverse effects. When antibiotics and antiviral drugs are combined, the individual side effects of each medication may be amplified, leading to an increased risk of gastrointestinal disturbances, neurological complications, or liver and kidney dysfunction.
To mitigate these risks, healthcare providers must carefully assess the patient's medical history, medication regimen, and potential interactions before prescribing a combination of antibiotics and antiviral drugs. Frequent monitoring of liver and kidney function, electrolyte levels, and clinical symptoms is essential to identify and manage any adverse reactions promptly.
In some cases, alternative treatment options or dose adjustments may be necessary to minimize the risk of adverse events. Additionally, patient education and close collaboration between healthcare providers, pharmacists, and patients are crucial in ensuring the safe and effective use of these medications.
As with any medical treatment, the decision to combine antibiotics and antiviral drugs should be made on a case-by-case basis, weighing the potential benefits against the risks. Ongoing research and clinical studies continue to shed light on the complex interactions between these two classes of medications, providing healthcare professionals with the knowledge and tools to optimize patient care and minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
Have you or someone you know experienced any challenges or adverse effects when taking antibiotics and antiviral drugs concurrently? Share your experiences and insights to contribute to the understanding of this important topic.