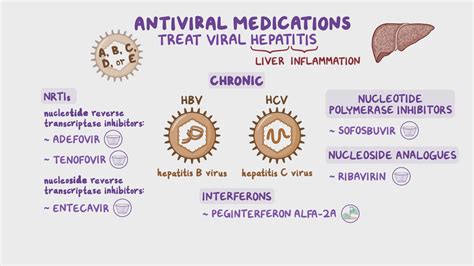
Battling Severe Infections: Exploring the Potential Benefits of Combining Antibiotics and Antiviral Therapy
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Mar-15
When faced with a severe infection, healthcare providers often find themselves navigating a complex web of treatment options. One strategy that has garnered increasing attention is the use of combined antibiotic and antiviral therapy. But is this approach truly beneficial, or does it simply complicate an already challenging situation?
The rationale behind combining these two classes of medications lies in the synergistic effects they can potentially exert. Antibiotics are well-known for their ability to target and eliminate bacterial pathogens, while antivirals are designed to disrupt the replication and spread of viruses. By employing both, the theory suggests that the duo can work in tandem to combat the multifaceted nature of severe infections, which often involve a complex interplay between bacterial and viral components.
Proponents of this combined therapy argue that it can lead to improved patient outcomes, particularly in cases where the infection has progressed to a critical stage. The argument is that by simultaneously addressing the bacterial and viral aspects of the disease, clinicians can potentially achieve more robust and rapid clinical improvement, ultimately reducing the risk of complications and improving overall prognosis.
However, the opponents of this approach caution that the added complexity of incorporating both antibiotics and antivirals may also introduce additional challenges. Concerns have been raised about the potential for increased drug interactions, heightened side effects, and the risk of developing antimicrobial resistance – a growing global health concern. These factors, they argue, must be carefully weighed against the potential benefits.
Ultimately, the debate surrounding the efficacy of combining antibiotics and antiviral therapy in severe infections remains an active area of research and clinical discussion. While some studies have shown promising results, the scientific community continues to grapple with the nuances of this treatment approach, seeking to strike the right balance between the potential benefits and the possible drawbacks.
As healthcare providers strive to optimize patient care, the question remains: Is adding antibiotics to antiviral therapy truly beneficial in managing severe infections, or does it introduce more complexity than it solves? The answer, it seems, lies in the careful evaluation of each individual case, the underlying pathogen, and the patient's unique clinical profile. Only through continued research, robust clinical trials, and open dialogues among medical professionals can we hope to unravel the complexities of this intriguing treatment strategy.