Sequential vs. simultaneous therapy: Which is more effective?
Debate the efficacy of sequential therapy versus simultaneous administration of antibiotics and antivirals.
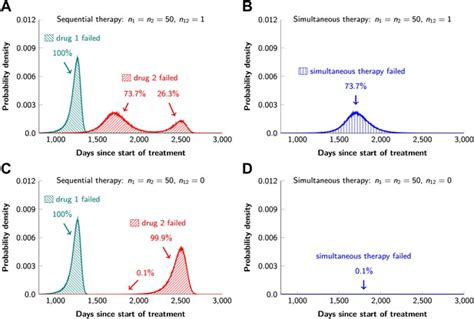
The age-old question of whether sequential or simultaneous therapy is more effective has long been a topic of debate among medical professionals. When it comes to the administration of antibiotics and antivirals, the choice between these two approaches can significantly impact patient outcomes. Let's delve into the nuances of this discussion and explore the pros and cons of each approach.
Sequential therapy, as the name suggests, involves the administration of one medication, typically an antibiotic, followed by the introduction of another, such as an antiviral. The rationale behind this method is to allow the first medication to take effect and potentially pave the way for the second to be more effective. Proponents of sequential therapy argue that this approach can prevent the development of antimicrobial resistance, as the two medications work in a complementary manner, targeting different aspects of the infection.
On the other hand, advocates of simultaneous therapy contend that administering the antibiotic and antiviral concurrently can lead to a more rapid and comprehensive resolution of the underlying infection. This approach, they argue, can potentially reduce the risk of disease progression and minimize the window of opportunity for the pathogen to develop resistance. Additionally, simultaneous therapy may provide a more convenient and streamlined treatment regimen for patients, potentially improving adherence and overall outcomes.
The debate surrounding the superiority of one approach over the other has generated a wealth of research and clinical evidence. Studies have explored various factors, such as the specific infectious agents, the severity of the illness, and the individual patient characteristics, to determine the most effective strategy.
Recent meta-analyses have suggested that in certain viral infections, such as influenza, simultaneous administration of antivirals and antibiotics may indeed offer superior outcomes compared to sequential therapy. This may be due to the synergistic effects of the two medications, which can collectively enhance the body's immune response and limit the proliferation of the viral pathogen.
However, for bacterial infections, the evidence is more nuanced. Some studies have shown that sequential therapy can be more effective in preventing the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, particularly in cases of pneumonia or sepsis. By allowing the antibiotic to exert its full effect before introducing the antiviral, the risk of resistance development may be reduced.
Ultimately, the choice between sequential and simultaneous therapy should be made on a case-by-case basis, considering the specific clinical scenario, the patient's individual characteristics, and the local epidemiological patterns of antimicrobial resistance. Clinicians must weigh the potential benefits and risks of each approach, carefully balancing the need for rapid and comprehensive treatment with the long-term implications of antimicrobial stewardship.
As the debate continues, healthcare professionals and researchers will undoubtedly delve deeper into this complex topic, exploring new avenues for optimizing the use of antibiotics and antivirals in the fight against various infectious diseases. The ever-evolving landscape of medical science and the ongoing quest for improved patient outcomes will undoubtedly drive further investigations and discussions on this intriguing subject.
What do you believe is the most effective approach in your clinical practice? Share your insights and experiences with us.
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Mar-30
User comments
More Topics to Explore
Can sequential therapy improve treatment outcomes?
Discuss the effectiveness of using a sequence of antibiotics and antivirals in treating infections and diseases.
How does sequential therapy impact drug resistance?
Engage in a discussion on the relationship between sequential therapy and the development of antibiotic and antiviral resistance.
Exploring the role of sequential therapy in chronic infections
Share your knowledge on how sequential antibiotics and antivirals can be utilized in the long-term treatment of chronic infections.
Impact of sequential therapy on the gut microbiome
Examine the effects of sequential antibiotics and antivirals on the balance of gut flora and overall gut health.
Sequential therapy in the era of multidrug-resistant infections
Explore the role of sequential antibiotics and antivirals in combating multidrug-resistant infections.
Optimizing treatment outcomes with tailored sequential therapy regimens
Share insights on how customized sequential antibiotics and antivirals regimens can optimize treatment outcomes for patients.