The Rise of Antivirals and Their Potential Side Effects
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Mar-15
Antiviral medications have become increasingly prevalent in recent decades as we've faced the emergence of new viral threats like HIV, the flu, COVID-19 and more. These specialized drugs work by interfering with the replication process of viruses, helping the body fight off infection and mitigate symptoms. But while antivirals can be highly effective, they also come with the potential for various side effects.
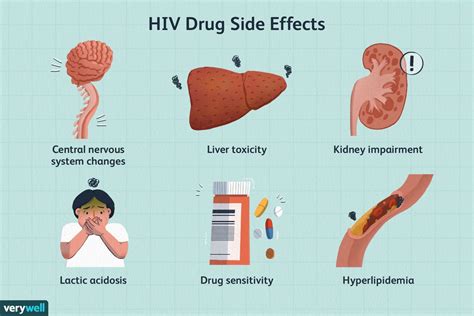
The specific side effects experienced depend on the particular antiviral drug, as well as the individual patient's biology and overall health status. However, some of the more commonly reported side effects of antiviral medications include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headaches, fatigue, dizziness, and insomnia. More severe side effects that occasionally occur include liver damage, kidney problems, and neurological issues like depression or anxiety.
For example, the antiviral drug Tamiflu (oseltamivir), which is commonly prescribed to treat influenza, has been known to cause nausea, vomiting, headaches, and diarrhea in some patients. Similarly, the antiviral drug Valtrex (valacyclovir), used to manage herpes simplex and shingles outbreaks, can potentially lead to side effects like headaches, stomach pain, and mood changes.
One of the reasons antiviral medications can have such a wide range of side effects is that they often work by disrupting the rapid replication of viruses - a process that can inadvertently impact healthy human cells and processes as well. The liver and kidneys, which are responsible for metabolizing and clearing medications from the body, are especially vulnerable to potential antiviral side effects.
1. Closely following dosage instructions and taking medications with food when recommended, to help reduce gastrointestinal side effects.
2. Staying hydrated, getting adequate rest, and avoiding alcohol, which can further strain the liver and kidneys.
3. Regularly monitoring any changes in mood, cognition, or physical symptoms and promptly reporting them to a healthcare provider.
4. Being proactive about managing side effects through over-the-counter remedies like anti-nausea medications, pain relievers, or sleep aids when appropriate.
5. Discussing alternative antiviral options with a doctor if side effects become unmanageable, as different drugs in this class can have varying side effect profiles.
Ultimately, the decision to take antiviral medications should involve a careful weighing of the potential benefits and risks for each individual patient. While side effects can be concerning, the consequences of untreated viral infections are often far more severe. With proper monitoring and management, most patients are able to tolerate antiviral treatments and achieve the desired therapeutic outcomes.
Have you or a loved one experienced side effects from taking antiviral medications? How did you work to mitigate those issues? We'd be curious to hear your perspective.