What are the implications of agricultural practices on Antibiotic Resistance?
Evaluate the impact of agricultural practices, including antibiotic use in livestock and crops, on the development and spread of antibiotic resistance and potential solutions.
Antibiotic Resistance: A Growing Concern Stemming from Agricultural Practices
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Mar-27
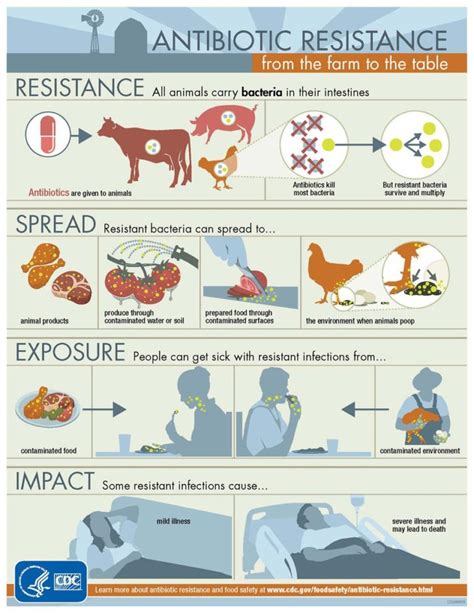
The widespread use of antibiotics in modern agriculture has become a growing concern, as it has been increasingly linked to the alarming rise of antibiotic resistance. As our reliance on these miracle drugs intensifies, the very foundations of our medical advancements are being threatened by the emergence of superbugs - bacteria and pathogens that have evolved to withstand even our most potent antimicrobial treatments.
At the heart of this issue lie the extensive agricultural practices that have become the norm in many parts of the world. From the routine administration of antibiotics to livestock for growth promotion and disease prevention, to the application of these drugs in crop cultivation, the agricultural sector has become a breeding ground for resistant microbes. As these resilient organisms proliferate, they can then spread beyond the farm, contaminating our food supply, water sources, and even entering human populations, posing a grave threat to public health.
The consequences of this phenomenon are far-reaching. Antibiotic-resistant infections can be significantly more difficult to treat, often requiring the use of stronger, more expensive, and potentially more toxic medications. This not only places a greater burden on healthcare systems, but also increases the risk of adverse outcomes for patients, potentially leading to prolonged illness, hospitalization, and even death.
Moreover, the emergence of superbugs has the potential to undermine the very foundation of modern medicine. Routine procedures, such as surgeries, organ transplants, and cancer treatments, often rely on the availability of effective antibiotics to prevent and manage infections. If these crucial drugs become ineffective, the safety and success of these life-saving interventions could be jeopardized.
1. Stricter Regulations on Antibiotic Use: Governments and regulatory bodies may need to implement more stringent policies regarding the use of antibiotics in livestock and crop production, limiting their use to only necessary and medically justified cases.
2. Promotion of Sustainable Farming Practices: Encouraging the adoption of alternative farming methods, such as organic agriculture, integrated pest management, and the use of probiotics or natural antimicrobials, could help reduce the reliance on antibiotics in the agricultural sector.
3. Improved Surveillance and Monitoring: Enhancing surveillance systems to track the emergence and spread of antibiotic-resistant microbes, both within the agricultural sector and in human populations, can help identify hotspots and inform targeted interventions.
4. Investment in Research and Development: Dedicating more resources to the development of new antibiotics, as well as alternative treatment and prevention strategies, could help replenish the dwindling arsenal of effective antimicrobial agents.
As we grapple with the complex implications of agricultural practices on antibiotic resistance, it is clear that a concerted effort is needed to address this pressing global challenge. By taking proactive steps to mitigate the spread of superbugs, we can safeguard the future of both our agricultural and healthcare systems, ensuring that the benefits of these life-saving medications continue to be available for generations to come.
User comments
More Topics to Explore
How can the One Health Approach combat Antibiotic Resistance?
Discuss the effectiveness of integrating the One Health Approach in addressing antibiotic resistance from a holistic perspective involving humans, animals, and the environment.
What role do veterinarians play in the fight against Antibiotic Resistance?
Explore the crucial role of veterinarians in combating antibiotic resistance through responsible antibiotic use in animals and the impact on human health.
Is consumer education key in addressing Antibiotic Resistance?
Delve into the significance of consumer education in curbing antibiotic resistance through proper antibiotic use, awareness of antibiotic stewardship, and understanding the implications of misuse.
How can improved hygiene practices help in reducing Antibiotic Resistance?
Examine the relationship between enhanced hygiene practices, such as hand hygiene and sanitation, in lowering the prevalence of antibiotic resistance and reducing the need for antibiotics.
Can probiotics be a solution to Antibiotic Resistance?
Explore the potential of probiotics as a solution to antibiotic resistance by promoting healthy gut flora, reducing the need for antibiotics, and combating antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
What role does legislation play in managing Antibiotic Resistance?
Analyze the importance of legislation in controlling antibiotic resistance through regulations on antibiotic use, prescription practices, surveillance, and enforcement mechanisms.
How can rapid diagnostics aid in the fight against Antibiotic Resistance?
Examine the benefits of rapid diagnostic tests in combatting antibiotic resistance by enabling targeted antibiotic treatment, reducing unnecessary prescriptions, and promoting antimicrobial stewardship.
Is international collaboration crucial in combating Antibiotic Resistance?
Discuss the significance of international collaboration among countries, organizations, and healthcare systems in addressing antibiotic resistance through data sharing, research partnerships, and coordinated global strategies.