Understanding the Crucial Distinction: Viral vs. Bacterial Infections
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Apr-11
When it comes to managing infections, distinguishing between viral and bacterial origins is a critical step in providing appropriate and effective treatment. This differentiation is not merely an academic exercise, but a cornerstone of responsible medical practice and patient care.
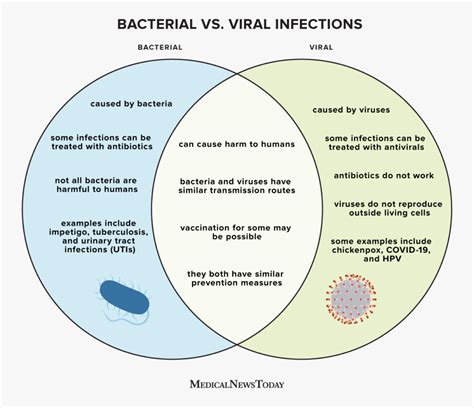
Viral infections and bacterial infections often present with similar symptoms, making the accurate diagnosis a challenge for healthcare providers. However, this distinction is paramount, as the underlying pathogens and the corresponding treatment approaches differ vastly.
Viral infections, such as the common cold, influenza, and COVID-19, are caused by viruses. These microscopic organisms hijack the host's cells to replicate, often triggering an immune response that manifests as fever, body aches, and respiratory distress. Viral infections are typically self-limiting, meaning the body's immune system can effectively combat them without the need for specific antiviral medications.
On the other hand, bacterial infections are caused by various bacteria, which are living, single-celled organisms. These infections can range from mild skin conditions, such as acne, to severe, life-threatening illnesses, like pneumonia or meningitis. Bacterial infections often require targeted antibiotic treatment to eliminate the causative bacteria and facilitate recovery.
The crucial distinction between viral and bacterial infections lies in the appropriate course of action. Antibiotics, while highly effective against bacterial infections, are ineffective against viruses and can even be harmful if prescribed unnecessarily. The overuse and misuse of antibiotics have contributed to the alarming rise of antimicrobial resistance, a global public health concern that compromises the effectiveness of these vital medications.
Accurate infection diagnosis is, therefore, essential to ensure patients receive the most appropriate treatment. Healthcare providers must carefully evaluate the patient's symptoms, medical history, and, in some cases, conduct laboratory tests to determine the underlying cause of the infection. This process allows them to make an informed decision on whether to prescribe antibiotics or manage the infection through supportive care and symptom management.
Adhering to evidence-based medical guidelines is crucial in this context. Professional organizations, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO), have developed comprehensive recommendations for the appropriate use of antibiotics, known as antimicrobial stewardship programs. These guidelines help healthcare providers make informed decisions, minimize the unnecessary use of antibiotics, and promote the responsible management of infections.
By differentiating between viral and bacterial infections, healthcare providers can avoid the pitfalls of overprescribing antibiotics, which can lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. This prudent approach not only benefits the individual patient but also contributes to the broader public health effort to combat the alarming rise of antimicrobial resistance.
In conclusion, the ability to accurately distinguish between viral and bacterial infections is a fundamental aspect of effective patient care and responsible antimicrobial stewardship. As we continue to navigate the complex landscape of infectious diseases, this crucial distinction remains a cornerstone of evidence-based medicine, ensuring patients receive the most appropriate treatment and contributing to the overall health and well-being of our communities.
What are your thoughts on the importance of accurate infection diagnosis in the context of viral and bacterial infections? Share your insights and experiences in the comments below.
User comments
More Topics to Explore
How can we reduce antibiotic resistance in our communities?
Discuss strategies to combat antibiotic resistance at the community level and promote responsible antibiotic use to preserve the effectiveness of these crucial medicines.
What are the consequences of antibiotic misuse on global health?
Explore the far-reaching impacts of antibiotic misuse on global health, including the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and the potential threats to healthcare systems worldwide.
How can healthcare professionals educate patients about responsible antibiotic use?
Share insights on effective ways for healthcare professionals to educate patients about the appropriate use of antibiotics, including communication strategies and resources for promoting antibiotic stewardship.
What role can pharmacists play in combating antibiotic misuse?
Examine the valuable contributions that pharmacists can make in combatting antibiotic misuse through patient education, medication counseling, and promoting appropriate antibiotic usage.
How does antibiotic misuse impact vulnerable populations?
Explore the disproportionate impact of antibiotic misuse on vulnerable populations, including low-income communities, elderly individuals, and those with chronic illnesses, and discuss strategies to protect these groups from the consequences of antibiotic resistance.
What are the environmental implications of antibiotic misuse?
Examine the environmental repercussions of antibiotic misuse, such as antibiotic pollution in water systems, soil contamination, and the emergence of resistant bacteria in wildlife, and discuss sustainable practices to mitigate these environmental impacts.
How can parents ensure responsible antibiotic use for their children?
Share tips and guidance for parents on promoting responsible antibiotic use for their children, including seeking medical advice before antibiotic treatment, completing the full course of antibiotics, and preventing unnecessary prescriptions.
What innovations are shaping the future of antibiotic development?
Explore the latest advancements in antibiotic research and drug discovery, including novel technologies, alternative therapies, and precision medicine approaches that hold promise for combating antibiotic resistance and addressing unmet medical needs.