Understanding Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection FAQ
What is respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)?
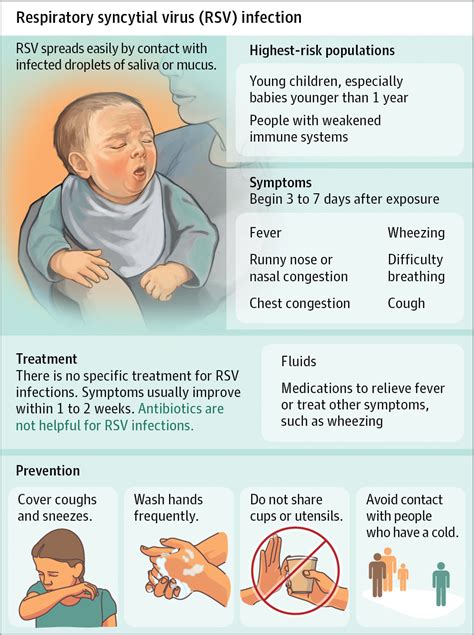
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a common virus that infects the airways and lungs. It is highly contagious and spreads easily. The main treatment for RSV infection is rest and plenty of fluids. Regular handwashing and good personal hygiene can stop RSV from spreading.
How does respiratory syncytial virus spread?
Respiratory syncytial virus enters the body through the eyes, nose or mouth. It spreads easily through the air on infected respiratory droplets. You or your child can become infected if someone with RSV coughs or sneezes near you. The virus also passes to others through direct contact, such as shaking hands.
Is respiratory syncytial virus contagious?
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a common virus that can infect your airways and lungs. It is highly contagious and spreads easily. RSV infections most often affect children under 2 years of age. What are the symptoms of RSV? Symptoms usually start 3 to 10 days after infection with RSV. Some people will also get an ear infection.
Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection References
If you want to know more about Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection, consider exploring links below:
What Is Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection
- https://www.abc.net.au/news/2023-05-15/what-is-rsv-symptoms-infectious-period-contagious-vaccine/102331104
- https://www.health.gov.au/diseases/respiratory-syncytial-virus-rsv-infection
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/respiratory-syncytial-virus/symptoms-causes/syc-20353098
- https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/respiratory-syncytial-virus-rsv
- https://www.health.nsw.gov.au/Infectious/factsheets/Pages/respiratory-syncytial-virus.aspx
- https://www.cdc.gov/rsv/index.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Respiratory_syncytial_virus
- https://www.rch.org.au/kidsinfo/fact_sheets/Respiratory_Syncytial_Virus_RSV/