Skin Structure Infections: Types and Treatment
Skin Structure Infections FAQ
What is skin and skin structure infection?
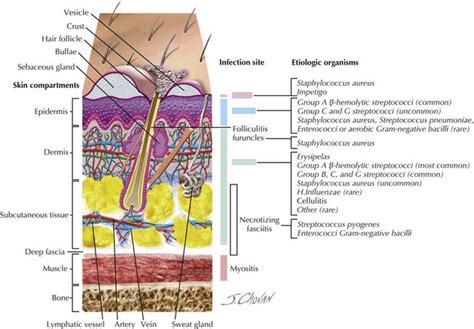
Indian J Dermatol. 2011 Sep-Oct; 56 (5): 510–512. A skin and skin structure infection is a bacterial infection of skin and associated tissues. It may be complicated skin and skin structure infection or uncomplicated skin and skin structure infection.
What is a bacterial skin infection?
Bacterial skin infections occur when bacteria enter through the surface of the skin. They can cause symptoms such as swelling and inflammation. Treatment may include topical or oral antibiotics. Experts classify bacterial skin infections as skin and soft tissue infections (SSTI) or acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI).
What are skin and skin structure infections (SSSIs)?
Skin and skin structure infections ( SSSIs ), also referred to as skin and soft tissue infections ( SSTIs ), or acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections ( ABSSSIs ), are infections of skin and associated soft tissues (such as loose connective tissue and mucous membranes ). [citation needed]
What causes a skin infection?
Skin infections occur when germs infect your skin or the soft tissues below the skin's surface. There are four main types of germs that can infect your skin: bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Anyone can develop a skin infection.
Skin Structure Infections References
If you want to know more about Skin Structure Infections, consider exploring links below:
What Is Skin Structure Infections
- https://www.healthline.com/health/skin-infection
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/bacterial-skin-infections
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skin_and_skin_structure_infection
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6451992/
- https://www.health.com/skin-infections-7968751
- https://www.msdmanuals.com/en-gb/professional/dermatologic-disorders/bacterial-skin-infections/overview-of-bacterial-skin-infections
- https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/skin-infection-signs
Skin Structure Infections Information
Explore Related Topics
Patient Perspectives on Combination Therapy for Resistant Infections
How do patients feel about undergoing combination therapy for resistant infections? Join the discussion to understand patient experiences and viewpoints!