Insight into Specific Bacterial Infections and Treatment
Specific Bacterial Infections FAQ
What is a bacterial infection?
Bacterial infections are any illness or condition caused by bacterial growth or poisons (toxins). You can get sick from getting harmful bacteria in your skin, gut (GI tract), lungs, heart, brain, blood or anywhere else in your body.
What are some common bacterial infections?
Common bacterial infections include: Campylobacter and Salmonella infections, common types of food poisoning. Cellulitis, boils and impetigo, skin infections. Pneumococcal disease, including ear and sinus infections and some types of pneumonia. Lyme disease, a disease spread by ticks. Bacterial vaginosis, an overgrowth of bacteria in your vagina.
Can bacteria cause a bacterial infection?
No, many bacteria don't cause infection. Some bacteria are even helpful. Many of the bacteria that live on your skin or in your body are normal and don't hurt you. These are called your resident flora . However, other bacteria that get on or in your body can attack it. How do you get a bacterial infection?
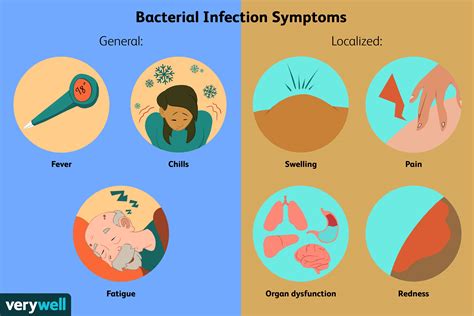
What are the symptoms of a bacterial infection?
The symptoms of a bacterial infection will usually depend on the type of bacterial infection you have and which body parts are most affected by a specific bacteria. However, most bacterial infections do share some common symptoms, including: Pain or discomfort in the affected body part (e.g., throat, joints, chest, ears, urethra, etc.)
Specific Bacterial Infections References
If you want to know more about Specific Bacterial Infections, consider exploring links below:
What Is Specific Bacterial Infections
- https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/bacterial-infections
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24189-bacterial-infection
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/what-is-a-bacterial-infection-770565
- https://www.health.com/bacterial-infection-8421214
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7149789/
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/bacterial-infection-symptoms
- https://medlineplus.gov/bacterialinfections.html
- https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/quick-facts-infections/bacterial-infections-overview/overview-of-bacteria
Specific Bacterial Infections Information
Explore Related Topics
How can we address antibiotic resistance in livestock and agriculture?
Examine the role of antibiotics in livestock farming and agriculture, and their contribution to the spread of antibiotic resistance. What measures can be taken to minimize the use of antibiotics in animal agriculture and prevent the transmission of resistant bacteria to humans? Share your insights on addressing antibiotic resistance in the livestock and agriculture sectors.
How can we prevent community-acquired antibiotic resistance?
Discuss strategies for preventing antibiotic resistance in community settings and share effective prevention methods.