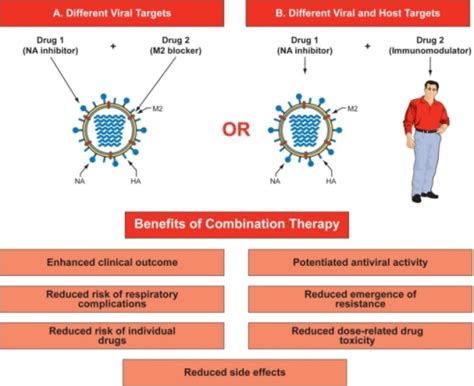
The Potential of Combination Therapy to Overcome Antiviral Resistance
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Mar-24
With the growing threat of antiviral resistance posing challenges across various viral infections, the medical community is exploring innovative treatment strategies to stay one step ahead. One promising approach that has gained considerable attention is the use of combination therapy - the concurrent administration of two or more antiviral medications with distinct mechanisms of action.
The rationale behind combination therapy lies in the ability to target multiple viral pathways simultaneously, making it harder for the virus to develop resistance. By attacking the virus through complementary mechanisms, the likelihood of a single mutation conferring resistance to all the drugs in the regimen is significantly reduced. This approach has been successfully implemented in the management of other complex infectious diseases, such as HIV and tuberculosis, where combination therapies have demonstrated improved treatment outcomes and reduced the risk of resistance emergence.
In the context of viral infections, combination therapy has shown promising results in combating influenza, hepatitis C, and even COVID-19. By pairing antiviral agents with different targets and modes of action, clinicians can create a multifaceted defense against the virus, hindering its ability to adapt and survive.
For instance, in the treatment of influenza, the combination of a neuraminidase inhibitor (e.g., oseltamivir or zanamivir) and a polymerase inhibitor (e.g., baloxavir marboxil) has been found to be more effective in reducing viral load and alleviating symptoms compared to monotherapy. This synergistic approach helps to overcome the potential for resistance development, which has been observed with the use of single-drug regimens.
Similarly, in the management of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, the advent of direct-acting antiviral (DAA) combination therapies has revolutionized the treatment landscape. By combining multiple DAAs with complementary mechanisms, such as NS5A inhibitors, NS5B polymerase inhibitors, and protease inhibitors, clinicians can achieve higher sustained virological response (SVR) rates and reduce the risk of treatment failure due to resistance.
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has also prompted exploration of combination therapy as a strategy to combat the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Various clinical trials are investigating the efficacy of combining antiviral agents, such as remdesivir, with immunomodulatory drugs or other antiviral compounds. The goal is to leverage the combined effects of these interventions to suppress viral replication, mitigate disease progression, and potentially overcome the emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants that may exhibit increased resistance to individual therapies.
While the potential benefits of combination therapy in addressing antiviral resistance are promising, it is important to acknowledge the challenges associated with this approach. Designing and implementing effective combination regimens requires a deep understanding of the viral targets, pharmacokinetics, and potential drug-drug interactions. Additionally, the increased complexity of combination therapy can pose logistical and adherence challenges for patients, potentially impacting the real-world effectiveness of the treatment.
Furthermore, the development and regulatory approval of combination therapies can be a lengthier and more costly process compared to single-agent therapies. Careful consideration must be given to the selection of the most appropriate antiviral agents, their dosing, and the potential for synergistic or antagonistic effects.
Nonetheless, the continued research and clinical experience with combination therapy hold the promise of overcoming the persistent challenge of antiviral resistance. As the scientific community works to stay ahead of the evolutionary curve, the strategic use of combination therapy may prove to be a crucial tool in the arsenal against viral infections.
What are your thoughts on the potential of combination therapy in combating antiviral resistance? Share your insights and experiences in the comments below.