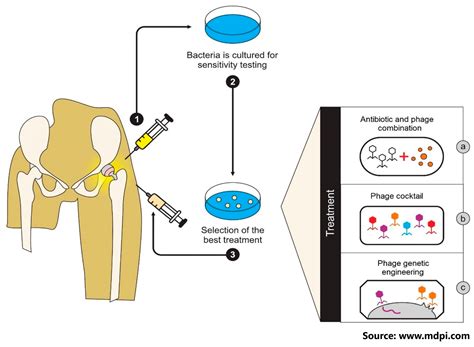
Can combination therapy overcome drug resistance in infections?
Examine the efficacy of combination therapy in overcoming drug resistance in infections, discussing how using multiple medications simultaneously can combat resistant strains.
Combatting the Challenge of Drug Resistance: The Promise of Combination Therapy
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Mar-21
As the global healthcare landscape grapples with the ever-evolving threat of drug-resistant infections, researchers and clinicians have turned their attention to innovative treatment strategies that hold the potential to turn the tide. One such approach that has garnered significant interest is the use of combination therapy – the simultaneous administration of multiple medications to tackle a single infection.
The rise of antibiotic resistance has become a pressing public health concern, with numerous pathogens developing the ability to evade the effects of previously effective drugs. This phenomenon, driven by factors such as the overuse and misuse of antibiotics, has led to the emergence of superbugs – strains of bacteria that are resistant to a wide range of antimicrobial agents. Faced with this challenge, the medical community has been driven to explore new avenues that can overcome these resistant strains.
Enter combination therapy, a multi-pronged approach that aims to harness the synergistic effects of multiple drugs. The underlying premise is that by targeting different mechanisms or pathways within the infectious agent, the chances of developing resistance can be significantly reduced. This strategy has shown promising results in various clinical settings, as evidenced by a growing body of research.
A study published in the *Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy* examined the use of combination therapy in the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections. The researchers found that the combined use of antibiotics, such as vancomycin and rifampicin, resulted in improved clinical outcomes and a lower incidence of resistance development compared to single-drug regimens.
Similarly, a review article in the *Lancet Infectious Diseases* highlighted the benefits of combination therapy in tackling multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. By employing a cocktail of several antitubercular drugs, clinicians were able to achieve higher treatment success rates and minimize the risk of further resistance emergence.
The mechanisms by which combination therapy overcomes drug resistance are multifaceted. First, the simultaneous use of multiple drugs with distinct mechanisms of action can make it more challenging for pathogens to develop resistance to all the components simultaneously. Second, certain drug combinations can have a synergistic effect, where the combined potency exceeds the sum of the individual drugs. This can lead to improved bacterial killing and reduced chances of resistance development.
Third, combination therapy may also disrupt the ability of pathogens to deploy efflux pumps – specialized mechanisms that expel antimicrobial agents from the cell, rendering them ineffective. By targeting multiple pathways, the chances of circumventing these resistance mechanisms are significantly reduced.
Despite the promising data, the implementation of combination therapy is not without its challenges. Clinicians must navigate the complexities of managing multiple medications, ensuring appropriate dosing, and monitoring for potential drug interactions and side effects. Additionally, the development and testing of new drug combinations can be a lengthy and resource-intensive process, requiring extensive clinical trials and regulatory approvals.
Nevertheless, the potential benefits of combination therapy in overcoming drug resistance are undeniable. As the global healthcare community continues to grapple with the growing threat of antimicrobial resistance, this treatment approach holds the promise of a more robust and sustainable solution. By leveraging the synergistic effects of multiple drugs, clinicians may be able to turn the tide and regain the upper hand in the fight against stubborn, drug-resistant infections.
What do you think about the potential of combination therapy in combating antimicrobial resistance? Share your insights and experiences in the comments below.
User comments
More Topics to Explore
How do bacteria develop resistance to antibiotics?
Explore the various mechanisms through which bacteria develop resistance to antibiotics, shedding light on the importance of understanding these processes in combating resistant infections.
What are the challenges in managing drug-resistant infections?
Delve into the complexities and hurdles faced in managing drug-resistant infections, discussing the various challenges healthcare professionals encounter in treating such cases.
How does antibiotic misuse contribute to drug resistance?
Uncover the correlation between antibiotic misuse and the development of drug resistance, emphasizing the importance of responsible antibiotic use in preventing resistant infections.
Is genetic mutation a key factor in antibiotic resistance?
Investigate the role of genetic mutation as a fundamental factor in antibiotic resistance, highlighting how mutations in bacterial DNA can lead to resistance development.
What are the differences between intrinsic and acquired drug resistance?
Differentiate between intrinsic and acquired drug resistance, discussing the inherent vs. acquired mechanisms bacteria employ to resist antibiotics, offering insights into treatment strategies.
How can we prevent the emergence of multidrug-resistant infections?
Identify preventive measures to curb the emergence of multidrug-resistant infections, highlighting strategies and practices that can help mitigate the spread of resistant strains.
Are there natural alternatives to antibiotics for combating resistant infections?
Explore the realm of natural alternatives to antibiotics for treating drug-resistant infections, discussing the potential of herbal remedies, probiotics, and other non-pharmaceutical options.
How do biofilms contribute to antibiotic resistance in infections?
Examine the role of biofilms in promoting antibiotic resistance within infections, uncovering how these microbial communities shield bacteria from antibiotic effects, posing challenges in treatment.
What role do efflux pumps play in antibiotic resistance mechanisms?
Explore the significance of efflux pumps in antibiotic resistance mechanisms, elucidating how these transport proteins help bacteria expel antibiotics, reducing their effectiveness.