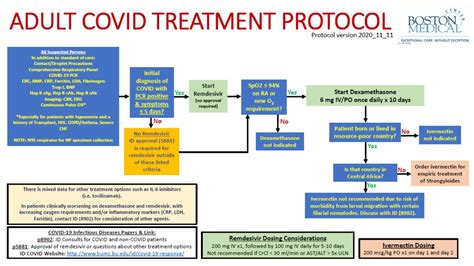
Navigating the Complexities of Simultaneous Antibiotics and Antivirals Administration
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Mar-21
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, clinicians are often faced with the challenge of managing complex treatment protocols involving the concurrent use of antibiotics and antivirals. This delicate balance is crucial, as the effective administration of these two vital classes of medications can significantly impact patient outcomes, particularly in the management of severe or life-threatening infections.
The rationale for the concurrent use of antibiotics and antivirals lies in the synergistic potential of these therapies. Antibiotics target bacterial infections, while antivirals are designed to combat viral pathogens. In certain clinical scenarios, such as in the case of co-infections or opportunistic infections, the combined application of these treatments can enhance the overall efficacy and improve the chances of successful patient recovery.
However, the simultaneous administration of antibiotics and antivirals is not without its nuances and potential risks. Clinicians must carefully consider factors such as pharmacokinetic interactions, dosage adjustments, and potential adverse effects to ensure the safe and effective use of these medications.
One key consideration in the administration of antibiotics and antivirals is the timing and sequencing of these therapies. In some cases, it may be beneficial to initiate antibiotics first, followed by the introduction of antivirals, to address the immediate bacterial threat and then target the underlying viral infection. Conversely, in other scenarios, starting with antivirals may be the preferred approach, particularly in the context of severe viral infections where the prompt control of the viral load is of paramount importance.
Additionally, healthcare providers must be vigilant in monitoring for potential drug interactions between antibiotics and antivirals, as these can significantly impact the efficacy and safety of both treatment modalities. Careful selection of appropriate medication combinations, appropriate dose adjustments, and close monitoring of laboratory values and clinical response are essential to mitigate the risks associated with such interactions.
Another crucial aspect of effective protocols for simultaneous antibiotics and antivirals administration is the importance of individualized patient care. Each patient's unique clinical presentation, underlying medical conditions, and response to therapy must be carefully evaluated to tailor the treatment approach accordingly. This personalized approach can help optimize the therapeutic outcomes and minimize the risk of adverse events.
In conclusion, the effective administration of antibiotics and antivirals concurrently is a complex and multifaceted challenge that requires a comprehensive understanding of pharmacology, clinical pharmacology, and patient-specific factors. By adhering to well-established protocols, closely monitoring patients, and regularly reviewing the latest evidence-based guidelines, healthcare providers can navigate this delicate balance and deliver the most appropriate and effective treatment for their patients.
As medical professionals, we must continue to explore and refine the strategies for the concurrent use of antibiotics and antivirals, ensuring that our patients receive the most optimal and safe care. What other considerations or experiences have you encountered in managing this intricate balance? We welcome your insights and perspectives to further advance the field of simultaneous antibiotics and antivirals administration.