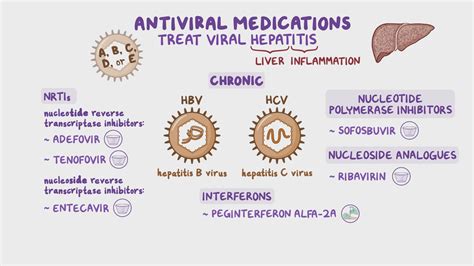
Administering Antibiotics and Antivirals Together: Weighing the Risks and Benefits
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Mar-18
The concurrent use of antibiotics and antivirals in medical treatment is a complex and often debated topic, as healthcare professionals must carefully consider the potential risks and benefits of this approach. While the combination of these two classes of medications can be an effective strategy in certain cases, it is essential to understand the potential interactions and possible adverse effects that may arise.
Antibiotics, which are designed to target and eliminate bacterial infections, and antivirals, which are used to treat viral infections, can sometimes be prescribed together to address complex medical conditions. This may occur when a patient is experiencing a bacterial infection that is exacerbating or complicating a pre-existing viral infection, or when a weakened immune system leaves the individual vulnerable to multiple types of pathogens.
One of the primary concerns with the co-administration of antibiotics and antivirals is the potential for drug interactions. Certain antibiotics, such as rifampicin, can induce the metabolic enzymes that break down antivirals, leading to reduced effectiveness of the antiviral medication. Conversely, some antivirals, like ritonavir, can inhibit the enzymes responsible for metabolizing certain antibiotics, resulting in increased drug concentrations and an elevated risk of adverse effects.
Additionally, the simultaneous use of these medications may increase the risk of adverse side effects, including gastrointestinal disturbances, liver toxicity, and kidney problems. Patients with pre-existing medical conditions, such as kidney or liver disease, may be particularly vulnerable to these complications, necessitating careful monitoring and dose adjustments.
However, it is important to note that in some cases, the benefits of combining antibiotics and antivirals may outweigh the potential risks. For instance, in the treatment of HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infection, the use of antiretroviral therapy often involves the concurrent administration of multiple antivirals, which may be accompanied by the addition of antibiotics to address opportunistic infections.
Furthermore, the emergence of antimicrobial resistance, where bacteria and viruses develop the ability to evade the effects of certain medications, has led healthcare providers to explore innovative treatment approaches. In some instances, the strategic combination of antibiotics and antivirals may be necessary to overcome these challenges and provide effective care.
To ensure the safe and effective use of antibiotics and antivirals, healthcare professionals must carefully evaluate each patient's individual circumstances, including their medical history, the nature of the infections, and any pre-existing conditions. Comprehensive monitoring, close collaboration between healthcare providers, and patient education are crucial in mitigating the risks associated with the co-administration of these medications.
As the medical landscape continues to evolve, the interplay between antibiotics and antivirals in clinical practice will undoubtedly remain a topic of ongoing research and discussion. By staying informed and prioritizing patient safety, healthcare providers can navigate this complex landscape and provide the best possible care for their patients.