How can healthcare professionals improve the accuracy of antimicrobial susceptibility testing results?
Share best practices, strategies, and tips for enhancing the precision and reliability of antimicrobial susceptibility testing outcomes. Discuss the role of proper specimen collection, laboratory techniques, and interpretation of results in optimizing patient care and antibiotic therapy.
Improving Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: A Critical Step for Effective Patient Care
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Mar-21
As healthcare professionals, ensuring the accuracy of antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) results is a paramount concern. AST plays a crucial role in guiding appropriate antibiotic therapy, which is vital for optimal patient outcomes and the fight against antimicrobial resistance. However, various factors can influence the reliability of AST, making it essential to employ best practices and strategies to enhance the precision of these crucial test results.
Proper specimen collection is the foundation for accurate AST. Ensuring that the sample is obtained from the appropriate site, free of contaminants, and transported promptly to the laboratory can significantly impact the validity of the test results. Healthcare professionals must follow standardized protocols for specimen collection, handling, and storage to minimize the risk of false-positive or false-negative findings.
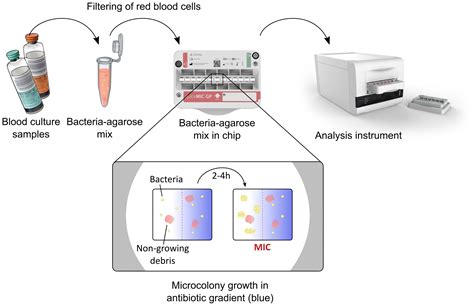
Once the specimen reaches the laboratory, the technicians must adhere to rigorous laboratory techniques to perform the AST. This includes adherence to established guidelines, such as those provided by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) or the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Meticulous attention to detail, from media preparation to inoculum standardization and incubation conditions, is crucial to obtaining reliable results.
The interpretation of AST results is another critical step in the process. Healthcare professionals must be well-versed in the nuances of interpreting minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values and zone diameter measurements, as well as understanding the clinical significance of the observed susceptibility patterns. Accurate interpretation can help guide appropriate antibiotic selection, dosing, and duration, ultimately improving patient care and reducing the risk of antimicrobial resistance.
In addition to these fundamental practices, healthcare professionals can explore various strategies to enhance the accuracy of AST results. One such approach is the implementation of molecular-based testing methods, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or whole-genome sequencing, which can provide more rapid and precise identification of antimicrobial resistance genes. These advanced techniques can complement traditional phenotypic AST, offering a more comprehensive understanding of a patient's infection and the corresponding antibiotic susceptibility profile.
Another strategy involves the use of automated or semi-automated AST platforms, which can standardize the testing process, reduce manual errors, and provide faster turnaround times for results. These systems often incorporate advanced data analysis algorithms, helping to improve the consistency and reliability of AST outcomes.
Furthermore, ongoing quality assurance and proficiency testing programs can help healthcare facilities identify any gaps or inconsistencies in their AST practices, enabling them to implement corrective measures and continuously improve their processes. Regular participation in such programs can ensure that AST results remain accurate and reliable over time.
By embracing these best practices, strategies, and tips, healthcare professionals can enhance the accuracy of antimicrobial susceptibility testing results, leading to more effective antibiotic therapy, better patient outcomes, and a stronger defense against the growing threat of antimicrobial resistance. As we strive to provide the highest quality of care, the optimization of AST remains a crucial step in our pursuit of excellence.
User comments
More Topics to Explore
How does antibiotic resistance affect antimicrobial susceptibility testing?
Discuss the impact of antibiotic resistance on the accuracy of antimicrobial susceptibility testing and the challenges it presents in treating bacterial infections. Share your insights and experiences on this important issue.
What are the key technologies used in antimicrobial susceptibility testing?
Delve into the various technologies such as automated systems, disk diffusion, and gradient diffusion used in antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Share the advantages, limitations, and future prospects of these technologies in predicting effective antibiotic treatments.
What are the emerging trends in antimicrobial susceptibility testing methods?
Explore the latest developments and advancements in antimicrobial susceptibility testing, including genotypic methods, MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, and rapid molecular techniques. Discuss the potential impact of these novel approaches on enhancing the speed and accuracy of identifying antibiotic-resistant pathogens.
Is there a correlation between biofilm formation and antimicrobial susceptibility testing?
Examine the relationship between biofilm-producing bacteria and their resistance to antimicrobial agents tested in standard susceptibility assays. Discuss the challenges posed by biofilm-associated infections in clinical settings and strategies to address biofilm-mediated antibiotic resistance.
What role does antimicrobial stewardship play in enhancing antimicrobial susceptibility testing?
Discuss the importance of antimicrobial stewardship programs in promoting rational antibiotic use, preserving efficacy, and combating resistance. Share insights on how antimicrobial stewardship initiatives can support accurate antimicrobial susceptibility testing and optimal antibiotic prescribing practices.
How do breakpoints influence the interpretation of antimicrobial susceptibility testing results?
Explain the concept of breakpoints in antimicrobial susceptibility testing and their significance in categorizing bacterial isolates as susceptible, intermediate, or resistant to specific antibiotics. Discuss the role of breakpoints in guiding clinical decision-making regarding antibiotic therapy and treatment outcomes.
What are the challenges in conducting antimicrobial susceptibility testing for atypical pathogens?
Explore the unique challenges and considerations involved in performing susceptibility testing for atypical pathogens like Mycoplasma, Chlamydia, and Legionella. Discuss the limitations of standard testing methods and the importance of tailored approaches to accurately assess antimicrobial susceptibility in these cases.
How can advances in data analytics enhance the accuracy of antimicrobial susceptibility testing?
Explore the potential applications of data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning in improving the precision and efficiency of antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Discuss how predictive modeling and big data analysis can optimize antibiotic selection, dosing regimens, and patient outcomes based on susceptibility test results.
What are the ethical considerations in antimicrobial susceptibility testing and reporting of results?
Reflect on the ethical dilemmas surrounding antimicrobial susceptibility testing, including issues of result interpretation, reporting, confidentiality, and patient autonomy. Discuss the principles of responsible antibiotic stewardship, patient consent, and equitable access to effective treatments in the context of antimicrobial susceptibility testing practices.