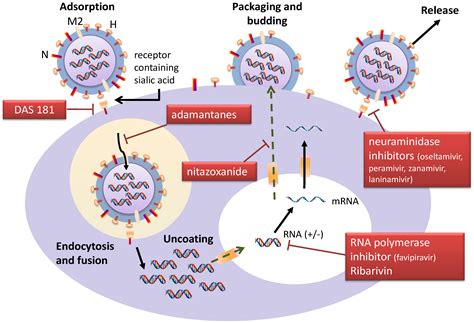
Antiviral Resistance: A Looming Challenge for Public Health
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Apr-06
The rapid evolution of viruses and the emergence of drug-resistant strains have become a growing concern in the world of public health. Antiviral resistance is a phenomenon where viruses develop the ability to evade or withstand the effects of antiviral medications, rendering them less effective or even ineffective in treatment and prevention efforts. As this issue continues to gain attention, it is crucial to examine the implications of antiviral resistance on public health strategies and interventions.
One of the primary impacts of antiviral resistance is its potential to undermine the effectiveness of existing public health interventions. When a virus becomes resistant to a particular antiviral drug, it can continue to spread and cause outbreaks, even in populations where the drug was previously used to control the infection. This can lead to higher rates of infection, increased severity of symptoms, and the need for alternative and often more expensive treatment options.
Moreover, the development of antiviral resistance can have far-reaching consequences on disease surveillance and outbreak management. As resistant strains emerge, public health authorities must adapt their monitoring and response strategies to detect and contain these new variants. This may require the development of more sophisticated diagnostic tools, the implementation of enhanced surveillance systems, and the implementation of alternative treatment and prevention measures.
Another significant implication of antiviral resistance is its potential to exacerbate health inequalities. Vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, immunocompromised individuals, and those with limited access to healthcare, may be disproportionately affected by the spread of resistant viruses. This can further strain already overburdened healthcare systems and lead to poorer health outcomes for these vulnerable groups.
In response to the challenge of antiviral resistance, public health strategies must evolve and adapt. One key approach is the implementation of antimicrobial stewardship programs, which aim to promote the responsible and prudent use of antiviral medications. These programs can help to reduce the selective pressure that drives the development of resistant strains, while also ensuring that these vital medications remain effective for those who need them.
Additionally, the development of new antiviral drugs and the exploration of alternative treatment approaches, such as combination therapies and the use of host-targeted therapies, can help to mitigate the impact of antiviral resistance. Investing in research and development in this area can be crucial for maintaining the arsenal of tools available to combat emerging viral threats.
Furthermore, the integration of public health education and awareness campaigns can empower individuals and communities to understand the risks of antiviral resistance and take appropriate measures to prevent its spread. This may include promoting good hygiene practices, encouraging vaccination, and advocating for responsible antimicrobial use.
As the world grapples with the ongoing challenges posed by antiviral resistance, it is clear that a multifaceted and collaborative approach is needed to address this issue. By leveraging the latest scientific advancements, implementing effective public health strategies, and fostering global cooperation, we can work towards a future where the threat of antiviral resistance is effectively managed and the health of our communities is better protected.
So, what steps can be taken to enhance public health strategies in the face of antiviral resistance? How can we ensure that our interventions remain effective and equitable in the face of this growing challenge?