Combating the Threat of Antiviral Resistance in Animal Health
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Mar-18
As our understanding of viral infections and the development of effective antiviral therapies continues to evolve, the emergence of antiviral resistance poses a growing challenge in the field of veterinary medicine. This complex issue warrants our careful consideration, as the implications of antiviral resistance can profoundly impact the health and well-being of animals under our care.
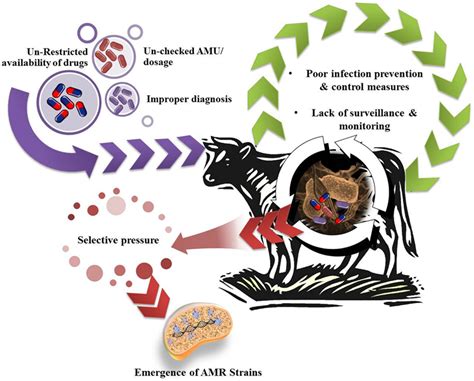
At the heart of this concern lies the ability of viruses to adapt and circumvent the protective measures we put in place. Antiviral resistance occurs when a virus develops genetic mutations that enable it to evade the action of antiviral drugs, rendering these once-effective treatments less potent or even completely ineffective. This phenomenon is not limited to a specific viral strain or species; it can manifest across a diverse range of animal pathogens, from avian influenza to feline immunodeficiency virus.
The consequences of antiviral resistance in the animal health sector can be far-reaching. As resistant viral strains emerge, veterinarians may find themselves increasingly limited in their therapeutic options, leading to prolonged illness, increased suffering, and potentially higher mortality rates among affected animals. This not only compromises the well-being of individual animals but can also have broader implications for herd or population-level health, as resistant viruses can spread more easily and potentially infect a greater number of susceptible hosts.
Moreover, the rise of antiviral resistance can have significant economic ramifications for animal owners, livestock producers, and the veterinary industry as a whole. Increased treatment costs, reduced productivity, and the potential for outbreaks that disrupt food supply chains are all potential outcomes that must be carefully considered.
To mitigate the risks posed by antiviral resistance, a multifaceted approach is required. Veterinary professionals must remain vigilant in monitoring for the emergence of resistant viral strains, utilizing advanced diagnostic tools and surveillance methods to detect these trends early on. Careful antimicrobial stewardship, including the judicious use of antiviral medications, can help slow the development and spread of resistance.
Additionally, investment in the research and development of novel antiviral therapies and alternative treatment strategies, such as combination therapies or the exploration of natural compounds, may help diversify the arsenal available to veterinarians. Enhancing biosecurity measures and promoting preventive care, including vaccination programs, can also play a crucial role in reducing the overall burden of viral infections and the selective pressure that contributes to the rise of antiviral resistance.
As we navigate the complex landscape of animal health and viral infections, the challenge of antiviral resistance serves as a stark reminder of the need for continued vigilance, innovative thinking, and a collaborative approach among researchers, veterinary professionals, and policymakers. By addressing this issue proactively, we can strive to safeguard the well-being of the animals entrusted to our care and ensure the long-term sustainability of veterinary medicine.
What strategies do you believe are most effective in mitigating the impact of antiviral resistance on animal health and welfare? Share your insights and experiences in the comments below.