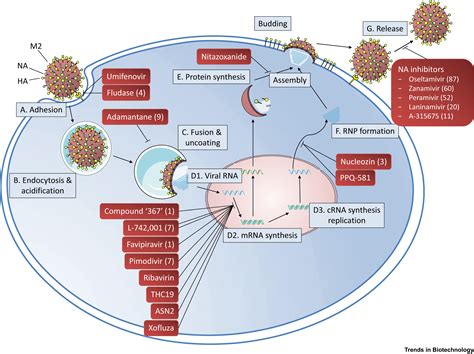
Monitoring Antiviral Resistance: Unveiling the Methods Behind the Surveillance
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Mar-18
Viruses, those microscopic invaders, have a remarkable ability to adapt and evolve, often rendering our antivirals ineffective. As the battle against viral infections rages on, healthcare professionals and researchers have developed a suite of surveillance methods to stay one step ahead of these ever-changing foes. In this article, we'll delve into the main techniques used to monitor antiviral resistance, exploring their strengths, limitations, and the critical insights they provide.
At the forefront of this endeavor lies genotypic testing, a molecular approach that examines the genetic makeup of viruses. By analyzing the specific mutations present in a virus's genetic code, researchers can identify the potential for resistance to certain antivirals. This method offers a rapid and cost-effective way to screen for resistance, allowing healthcare providers to make informed treatment decisions. However, its limitations lie in the fact that not all genetic changes are directly linked to resistance, and the interpretation of results can be complex.
Complementing genotypic testing, phenotypic testing provides a functional assessment of a virus's susceptibility to antivirals. This approach involves exposing the virus to varying concentrations of a specific antiviral and measuring its ability to replicate. By determining the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) required to inhibit viral growth, researchers can gauge the virus's level of resistance. Phenotypic testing offers a more direct measure of resistance, but it is generally more time-consuming and labor-intensive than genotypic testing.
Stepping beyond individual-level analysis, epidemiological surveillance plays a crucial role in monitoring antiviral resistance trends on a broader scale. By collecting and analyzing data from various healthcare settings, researchers can identify patterns of resistance, track the emergence and spread of resistant strains, and assess the effectiveness of antiviral therapies at a population level. This approach is essential for informing public health policies and guiding the development of new antiviral drugs.
In recent years, the field of molecular techniques has introduced sophisticated tools that further enhance our understanding of antiviral resistance. Methods like next-generation sequencing (NGS) and digital PCR enable the rapid and comprehensive analysis of viral genomes, allowing for the detection of even rare or complex resistance mutations. These advanced techniques offer unparalleled resolution, but they also require specialized expertise and infrastructure, often making them less accessible in resource-limited settings.
As we navigate the ever-evolving landscape of antiviral resistance, it's crucial to recognize that no single surveillance method holds all the answers. Rather, it is the strategic integration of these diverse approaches that provides the most robust and reliable insights. By employing a multifaceted surveillance framework, healthcare professionals and researchers can stay vigilant, anticipate emerging threats, and ultimately, strengthen our arsenal in the fight against viral infections.
So, what lies ahead for antiviral resistance surveillance? As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more sophisticated tools and techniques emerge, empowering us to stay one step ahead of these resilient viruses. But the true challenge lies in ensuring that these methods are accessible and widely adopted, enabling healthcare systems around the world to safeguard the health and well-being of their communities. The battle against antiviral resistance is far from over, but with a comprehensive surveillance strategy, we can navigate this complex landscape with greater confidence and resilience.