Does the Route of Administration Affect Antibiotic Pharmacodynamics?
Examine how different routes of antibiotic administration can influence pharmacodynamics. Discuss the implications of administration methods on antibiotic efficacy and absorption rates.
Does the Route of Administration Affect Antibiotic Pharmacodynamics?
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Apr-02
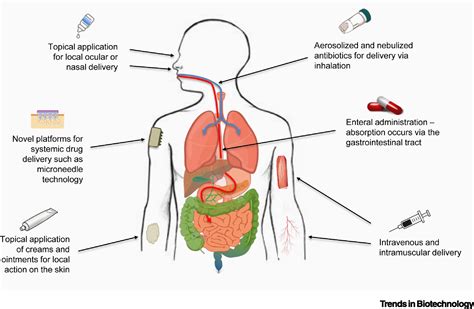
The administration of antibiotics is a critical aspect of effective antimicrobial therapy. Clinicians must carefully consider not only the choice of antibiotic but also the method of delivery, as the route of administration can significantly impact the drug's pharmacodynamics - the relationship between the drug concentration and its biological effects. Understanding how different routes affect antibiotic pharmacodynamics is essential for optimizing treatment outcomes and minimizing the risk of antimicrobial resistance.
One of the primary factors influenced by the route of administration is the bioavailability of the antibiotic - the amount of the active drug that reaches the systemic circulation and is available to exert its therapeutic effect. Oral administration, for example, requires the drug to be absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract, where it may encounter various physiological barriers that can limit its absorption rate and overall bioavailability. In contrast, intravenous (IV) administration bypasses these barriers, allowing for a more rapid and complete delivery of the antibiotic to the target sites.
The pharmacokinetic profile of an antibiotic, which describes the drug's absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination, can also vary significantly depending on the route of administration. Oral antibiotics may exhibit more variable and unpredictable pharmacokinetics due to factors such as food-drug interactions, gastric pH, and intestinal motility, whereas IV administration typically results in a more consistent and predictable pharmacokinetic profile.
The implications of these differences in pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics can be significant. For instance, certain beta-lactam antibiotics are known to exhibit time-dependent killing, meaning their efficacy is primarily determined by the duration of time the drug concentration remains above a certain threshold. In these cases, IV administration may be preferred over oral delivery, as it can ensure a more sustained and reliable concentration of the antibiotic at the target site.
On the other hand, fluoroquinolone antibiotics are often characterized by concentration-dependent killing, where the maximum drug concentration achieved is the primary determinant of their efficacy. For these antibiotics, the higher bioavailability associated with oral administration may be advantageous, as it can lead to a more robust peak concentration and improved antimicrobial activity.
The route of administration can also impact the tissue distribution of an antibiotic, which is particularly relevant for infections in specific anatomical locations. For example, intrathecal administration of antibiotics may be preferred for the treatment of central nervous system infections, as it can achieve higher drug concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid compared to systemic administration.
In summary, the route of antibiotic administration can have a significant impact on the pharmacodynamics and, consequently, the overall efficacy of antimicrobial therapy. Clinicians must carefully consider the unique pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles of different antibiotics when selecting the most appropriate administration method for a given patient and infection. By optimizing the route of administration, healthcare providers can maximize the chances of successful treatment and minimize the risks of treatment failure and antimicrobial resistance.
Does the route of administration truly play a crucial role in antibiotic pharmacodynamics, or are there other factors that should be taken into account when determining the optimal delivery method? Healthcare professionals and researchers are encouraged to share their insights and experiences in the comments section below.
User comments
More Topics to Explore
How do Antibiotics Affect Bacterial Growth Rates?
Discuss how antibiotics influence bacterial growth rates and the pharmacodynamics involved. Share your insights and knowledge on this crucial aspect of antibiotic action.
Are Antibiotics More Effective if Taken at Regular Intervals?
Delve into the importance of regular intervals in antibiotic dosing and its impact on effectiveness. Share your perspectives on the pharmacodynamics of dosing schedules.
How do Antibiotics Interact with Different Types of Bacteria?
Examine the varied interactions between antibiotics and different bacterial strains. Share examples and explanations of these pharmacodynamic interactions.
Can Antibiotics Lead to Antibiotic Resistance Through Pharmacodynamics?
Explore the fascinating connection between antibiotic use, pharmacodynamics, and the development of antibiotic resistance. Share your insights on how pharmacodynamics play a role in resistance development.
How do Antibiotics Target Specific Bacterial Cells?
Delve into the pharmacodynamics of antibiotics and how they target specific bacterial cells. Share your knowledge on the mechanisms behind this selective action.
Are Peak and Trough Levels Important in Antibiotic Therapy?
Discuss the significance of peak and trough levels in antibiotic therapy and their impact on pharmacodynamics. Share your insights on monitoring these levels for optimal treatment outcomes.
How do Antibiotics Maintain Therapeutic Concentrations in the Body?
Dive into the mechanisms by which antibiotics sustain therapeutic concentrations in the body and their implications on pharmacodynamics. Share your understanding of how doses are optimized for efficacy.
Can Combination Antibiotic Therapy Enhance Pharmacodynamic Effects?
Explore the potential benefits of combining antibiotics to enhance pharmacodynamic effects. Share examples of synergistic interactions and the rationale behind combining different antibiotics.
Is Antibiotic Efficacy Affected by Patient Factors in Pharmacodynamics?
Discuss how patient-specific factors can influence antibiotic efficacy through pharmacodynamics. Share your insights on variables such as age, weight, and health conditions in determining treatment outcomes.