Is Antibiotic Efficacy Affected by Patient Factors in Pharmacodynamics?
Discuss how patient-specific factors can influence antibiotic efficacy through pharmacodynamics. Share your insights on variables such as age, weight, and health conditions in determining treatment outcomes.
Antibiotic Efficacy and the Influence of Patient Factors
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Apr-12
As modern medicine continues to advance, the role of antibiotics in treating bacterial infections remains a critical component of healthcare. However, the efficacy of these life-saving drugs can be influenced by a variety of patient-specific factors, particularly when considering the complex principles of pharmacodynamics.
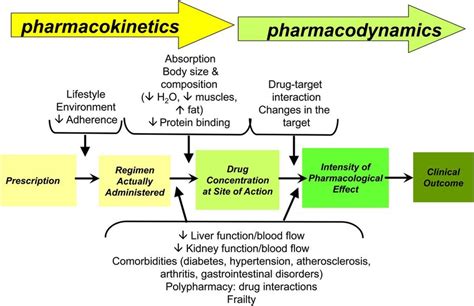
At the core of antibiotic efficacy is the relationship between the concentration of the drug and its ability to eliminate the target pathogenic bacteria. Pharmacodynamics seek to understand this dose-response relationship, taking into account variables such as the antibiotic's mechanism of action, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) required to halt bacterial growth, and the duration of time the drug concentration remains above the MIC.
But what happens when individual patient characteristics come into play? Emerging research suggests that factors like age, weight, and underlying health conditions can significantly impact the pharmacodynamics of antibiotics, ultimately affecting treatment outcomes.
Age is one of the most well-studied patient variables in this context. As the body ages, changes in organ function, protein binding, and drug distribution can alter the pharmacokinetics (absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination) of antibiotics. Older adults, for instance, often exhibit reduced renal clearance, leading to higher and more prolonged drug concentrations that may increase the risk of toxicity or adverse effects. Conversely, infants and young children may metabolize certain antibiotics more quickly, necessitating dosage adjustments to maintain therapeutic levels.
An individual's body weight can also be a crucial determinant of antibiotic efficacy. Patients who are overweight or obese may require higher doses to achieve the same drug concentrations as their normal-weight counterparts, as excess adipose tissue can affect the volume of distribution. Failing to account for these differences can result in suboptimal antibiotic levels, potentially contributing to treatment failure or the development of antibiotic resistance.
Furthermore, a patient's overall health status can significantly influence antibiotic pharmacodynamics. Individuals with impaired immune function, such as those with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or organ transplants, may respond differently to antibiotics due to altered drug metabolism or the unique nature of their infections. Similarly, patients with renal or hepatic dysfunction may experience changes in antibiotic clearance, requiring careful dosage monitoring and adjustment.
Complicating matters further, many patients present with multiple comorbidities, each with the potential to interact with and influence antibiotic pharmacodynamics. For example, a geriatric patient with diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and heart failure may require a completely different antibiotic regimen than a healthy young adult with a simple urinary tract infection.
To optimize antibiotic efficacy and minimize the risk of treatment failure or adverse events, healthcare providers must carefully consider these patient-specific factors. This often involves therapeutic drug monitoring, where the concentration of the antibiotic in the patient's bloodstream is measured to ensure it remains within the desired therapeutic range. Adjustments to the dose, frequency, or even the choice of antibiotic may be necessary to achieve the desired pharmacodynamic profile and clinical outcome.
As the battle against antibiotic resistance continues, understanding the complex interplay between patient characteristics and antibiotic pharmacodynamics becomes increasingly important. By tailoring antibiotic therapy to the individual, healthcare providers can enhance the likelihood of successful treatment, minimize the emergence of resistant strains, and ultimately improve patient outcomes.
The challenge of balancing antibiotic efficacy with patient-specific variables is an ongoing area of research and clinical exploration. As our understanding of these relationships deepens, the potential to deliver more personalized, effective, and safer antibiotic therapies continues to grow. What other patient-related factors might influence the pharmacodynamics of antibiotics, and how can healthcare professionals best navigate this complex landscape? The discussion remains open, inviting further insights and contributions from the scientific community.
User comments
More Topics to Explore
How do Antibiotics Affect Bacterial Growth Rates?
Discuss how antibiotics influence bacterial growth rates and the pharmacodynamics involved. Share your insights and knowledge on this crucial aspect of antibiotic action.
Are Antibiotics More Effective if Taken at Regular Intervals?
Delve into the importance of regular intervals in antibiotic dosing and its impact on effectiveness. Share your perspectives on the pharmacodynamics of dosing schedules.
How do Antibiotics Interact with Different Types of Bacteria?
Examine the varied interactions between antibiotics and different bacterial strains. Share examples and explanations of these pharmacodynamic interactions.
Can Antibiotics Lead to Antibiotic Resistance Through Pharmacodynamics?
Explore the fascinating connection between antibiotic use, pharmacodynamics, and the development of antibiotic resistance. Share your insights on how pharmacodynamics play a role in resistance development.
How do Antibiotics Target Specific Bacterial Cells?
Delve into the pharmacodynamics of antibiotics and how they target specific bacterial cells. Share your knowledge on the mechanisms behind this selective action.
Are Peak and Trough Levels Important in Antibiotic Therapy?
Discuss the significance of peak and trough levels in antibiotic therapy and their impact on pharmacodynamics. Share your insights on monitoring these levels for optimal treatment outcomes.
Does the Route of Administration Affect Antibiotic Pharmacodynamics?
Examine how different routes of antibiotic administration can influence pharmacodynamics. Discuss the implications of administration methods on antibiotic efficacy and absorption rates.
How do Antibiotics Maintain Therapeutic Concentrations in the Body?
Dive into the mechanisms by which antibiotics sustain therapeutic concentrations in the body and their implications on pharmacodynamics. Share your understanding of how doses are optimized for efficacy.
Can Combination Antibiotic Therapy Enhance Pharmacodynamic Effects?
Explore the potential benefits of combining antibiotics to enhance pharmacodynamic effects. Share examples of synergistic interactions and the rationale behind combining different antibiotics.