How do drug interactions impact the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics?
Investigate the potential interactions between antibiotics and other drugs, examining how these interactions can alter the pharmacokinetic profiles of antibiotics. Share examples of common drug interactions and their effects.
Navigating the Complex World of Antibiotic Pharmacokinetics: Unraveling the Impact of Drug Interactions
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Mar-21
As healthcare professionals, we are acutely aware of the crucial role that antibiotics play in combating the ever-evolving threat of infectious diseases. However, what many may not realize is the delicate dance that occurs between these essential medications and the myriad of other drugs patients may be taking. These drug interactions can significantly impact the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics, ultimately affecting their efficacy and safety.
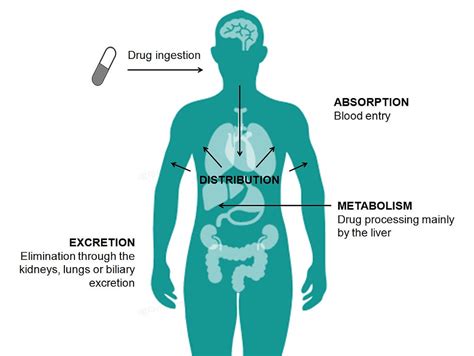
At the heart of this issue lies the complex web of metabolic pathways and transport mechanisms that govern the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of antibiotics within the human body. When other medications are introduced, they have the potential to interfere with these processes, altering the concentration and behavior of the antibiotic in the patient's system.
One prime example of this phenomenon is the interaction between rifampin, a potent antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis, and certain antiviral medications. Rifampin is a known inducer of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzyme system, which plays a crucial role in the metabolism of many drugs. When co-administered with HIV protease inhibitors or other antivirals that are substrates of the CYP enzymes, rifampin can significantly accelerate their metabolism, leading to subtherapeutic concentrations and reduced efficacy.
Conversely, the antibiotic clarithromycin, which is a CYP3A4 inhibitor, can impair the metabolism of certain immunosuppressant drugs, such as cyclosporine, leading to elevated drug levels and an increased risk of adverse effects. This is particularly relevant in transplant patients, where the delicate balance of immunosuppression must be carefully maintained.
Another area of concern is the impact of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) on the absorption of antibiotics. These medications, commonly prescribed for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or peptic ulcers, work by reducing stomach acid production. However, this alteration in gastric pH can impact the solubility and dissolution of certain antibiotics, such as fluoroquinolones and tetracyclines, potentially reducing their bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy.
It is crucial for healthcare providers to be vigilant in identifying and managing these drug interactions, as the consequences can be far-reaching. Suboptimal antibiotic concentrations can lead to treatment failure, the development of antibiotic resistance, and increased morbidity and mortality. Conversely, elevated antibiotic levels can increase the risk of adverse effects, from gastrointestinal disturbances to potentially life-threatening conditions.
As we continue to navigate the complex world of antibiotic pharmacokinetics, it becomes increasingly clear that a multifaceted approach is necessary. Comprehensive patient assessments, careful medication reviews, therapeutic drug monitoring, and close collaboration between healthcare professionals are all crucial components in ensuring the safe and effective use of antibiotics in the face of potential drug interactions.
By staying informed and proactive, we can better protect our patients and contribute to the global effort in the fight against infectious diseases. The impact of drug interactions on antibiotic pharmacokinetics is a topic that deserves ongoing research, discussion, and vigilance, as we strive to optimize patient outcomes and safeguard the efficacy of these essential medications.
What other factors do you believe healthcare providers should consider when managing the potential drug interactions of antibiotics? We welcome your insights and experiences in the comments below.
User comments
More Topics to Explore
How does renal dysfunction affect antibiotic pharmacokinetics?
Explore how renal dysfunction can impact the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics, including altered drug metabolism and clearance rates. Discuss strategies for dosage adjustment in patients with compromised renal function.
What role does protein binding play in the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics?
Delve into how protein binding affects the distribution and elimination of antibiotics in the body. Discuss the importance of considering protein binding in determining the dosage and efficacy of antibiotics.
Is there a connection between obesity and altered antibiotic pharmacokinetics?
Analyze how obesity can affect the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination of antibiotics in the body. Discuss the challenges in dosing antibiotics for obese patients and strategies to optimize therapy.
What are the considerations for pediatric antibiotic pharmacokinetics?
Examine the unique pharmacokinetic characteristics of antibiotics in pediatric patients, such as differences in drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Share insights into dosage adjustments and safety considerations for antibiotics in children.
How does age influence antibiotic pharmacokinetics in the elderly population?
Explore how age-related changes in physiology can impact the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics in the elderly. Discuss alterations in drug metabolism, renal function, and distribution in older patients, along with prescribing considerations.
What impact does liver disease have on antibiotic pharmacokinetics?
Examine the effects of liver disease on the metabolism and elimination of antibiotics, leading to altered pharmacokinetic profiles. Discuss challenges in prescribing antibiotics for patients with liver dysfunction and potential dosage adjustments.
How do suboptimal dosing regimens affect antibiotic pharmacokinetics?
Investigate the consequences of suboptimal dosing, such as underdosing or overdosing, on the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics. Explore the implications for treatment efficacy, antimicrobial resistance, and patient safety.
Can genetic factors influence antibiotic pharmacokinetics and response?
Explore how genetic variations can affect the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics, impacting drug metabolism, transport, and efficacy. Discuss the role of pharmacogenomics in personalized antibiotic therapy and its implications for patient care.
How does the route of administration affect antibiotic pharmacokinetics?
Explore the impact of different administration routes, such as oral, intravenous, and intramuscular, on the pharmacokinetic profiles of antibiotics. Discuss factors influencing drug absorption, distribution, and metabolism based on the route of administration.