How does age influence antibiotic pharmacokinetics in the elderly population?
Explore how age-related changes in physiology can impact the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics in the elderly. Discuss alterations in drug metabolism, renal function, and distribution in older patients, along with prescribing considerations.
Aging and Antibiotics: Understanding the Pharmacokinetic Challenges in the Elderly
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Mar-30
As we grow older, our bodies undergo a myriad of physiological changes that can significantly impact the way we respond to medications, including antibiotics. The elderly population, a group often defined as individuals aged 65 and above, face unique pharmacokinetic challenges that healthcare professionals must consider when prescribing these vital drugs.
At the heart of this issue lies the concept of pharmacokinetics, which describes how the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and eliminates a given medication. In the case of the elderly, age-related changes in various bodily functions can profoundly influence the way antibiotics behave within the system.
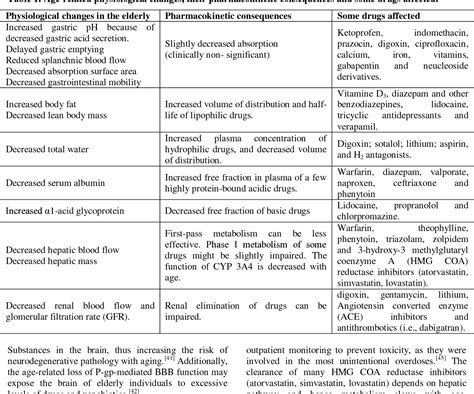
One of the primary factors to consider is the alteration in drug metabolism. As we age, the liver's ability to metabolize and break down certain medications can diminish, leading to a potentially higher concentration of the drug in the body. This is particularly relevant for antibiotics that undergo significant hepatic metabolism, as the elderly may be more susceptible to increased drug exposure and potentially adverse effects.
Furthermore, the declining renal function that often accompanies aging can also impact the elimination of antibiotics. Many antibiotics are primarily excreted through the kidneys, and as this filtration system becomes less efficient, the drug's clearance from the body may be impaired. This can result in a prolonged half-life and an increased risk of accumulation within the body, potentially leading to toxic levels and adverse reactions.
Another crucial factor is the altered drug distribution in the elderly population. Changes in body composition, such as a decrease in lean muscle mass and an increase in body fat percentage, can affect the volume of distribution for certain antibiotics. This, in turn, can impact the drug's concentration at the site of infection, potentially compromising its therapeutic efficacy.
Recognizing these age-related pharmacokinetic changes is essential for healthcare providers when prescribing antibiotics to the elderly. Careful dose adjustments and monitoring of drug levels may be necessary to ensure that the appropriate concentration of the antibiotic is achieved, while minimizing the risk of toxicity or subtherapeutic dosing.
Additionally, healthcare providers must consider the potential for drug interactions when prescribing antibiotics to the elderly, as this population often takes multiple medications to manage various health conditions. Certain antibiotics may interact with other drugs, leading to altered pharmacokinetics and the potential for adverse outcomes.
In conclusion, understanding the impact of aging on the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics is crucial for ensuring the safe and effective use of these essential medications in the elderly population. By staying vigilant to the physiological changes associated with aging and adapting their prescribing practices accordingly, healthcare professionals can help optimize the therapeutic benefits of antibiotics while minimizing the risks for this vulnerable patient group. As the global population continues to age, this knowledge will become increasingly important in providing comprehensive and personalized healthcare.
So, what other factors do you believe healthcare providers should consider when prescribing antibiotics to the elderly? Let us know your thoughts and experiences in the comments below.
User comments
More Topics to Explore
How does renal dysfunction affect antibiotic pharmacokinetics?
Explore how renal dysfunction can impact the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics, including altered drug metabolism and clearance rates. Discuss strategies for dosage adjustment in patients with compromised renal function.
What role does protein binding play in the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics?
Delve into how protein binding affects the distribution and elimination of antibiotics in the body. Discuss the importance of considering protein binding in determining the dosage and efficacy of antibiotics.
How do drug interactions impact the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics?
Investigate the potential interactions between antibiotics and other drugs, examining how these interactions can alter the pharmacokinetic profiles of antibiotics. Share examples of common drug interactions and their effects.
Is there a connection between obesity and altered antibiotic pharmacokinetics?
Analyze how obesity can affect the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination of antibiotics in the body. Discuss the challenges in dosing antibiotics for obese patients and strategies to optimize therapy.
What are the considerations for pediatric antibiotic pharmacokinetics?
Examine the unique pharmacokinetic characteristics of antibiotics in pediatric patients, such as differences in drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Share insights into dosage adjustments and safety considerations for antibiotics in children.
What impact does liver disease have on antibiotic pharmacokinetics?
Examine the effects of liver disease on the metabolism and elimination of antibiotics, leading to altered pharmacokinetic profiles. Discuss challenges in prescribing antibiotics for patients with liver dysfunction and potential dosage adjustments.
How do suboptimal dosing regimens affect antibiotic pharmacokinetics?
Investigate the consequences of suboptimal dosing, such as underdosing or overdosing, on the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics. Explore the implications for treatment efficacy, antimicrobial resistance, and patient safety.
Can genetic factors influence antibiotic pharmacokinetics and response?
Explore how genetic variations can affect the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics, impacting drug metabolism, transport, and efficacy. Discuss the role of pharmacogenomics in personalized antibiotic therapy and its implications for patient care.
How does the route of administration affect antibiotic pharmacokinetics?
Explore the impact of different administration routes, such as oral, intravenous, and intramuscular, on the pharmacokinetic profiles of antibiotics. Discuss factors influencing drug absorption, distribution, and metabolism based on the route of administration.