What are the considerations for pediatric antibiotic pharmacokinetics?
Examine the unique pharmacokinetic characteristics of antibiotics in pediatric patients, such as differences in drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Share insights into dosage adjustments and safety considerations for antibiotics in children.
Pediatric Antibiotic Pharmacokinetics: Navigating the Unique Needs of Young Patients
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Mar-27
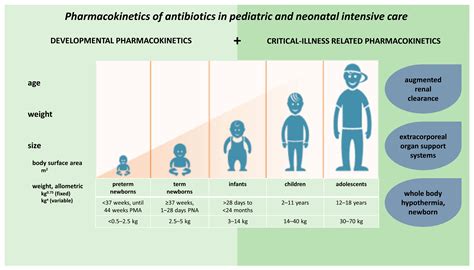
As healthcare professionals, we are constantly navigating the delicate balance between providing effective antibiotic treatment and ensuring the safety of our pediatric patients. The unique pharmacokinetic characteristics of antibiotics in children can pose significant challenges, requiring a deep understanding of how these medications behave within the developing bodies of young individuals.
At the core of this issue lies the fact that children are not simply small adults. Their bodies undergo profound physiological changes from birth through adolescence, each stage presenting its own set of pharmacokinetic considerations. Drug absorption, for instance, can be influenced by factors such as gastric pH, intestinal motility, and the presence of food, all of which may differ significantly in pediatric populations.
Moreover, the distribution of antibiotics can be affected by the varying composition of body fluids and tissues, as well as the development of organ systems responsible for metabolism and excretion. The liver and kidneys, for example, play crucial roles in the clearance of many antibiotics, and their maturation throughout childhood can significantly impact drug concentrations and dosing requirements.
Recognizing these unique pharmacokinetic differences is essential for dosage adjustments and ensuring the safety of antibiotic therapy in children. Inadequate dosing can lead to suboptimal treatment outcomes, while excessive dosing can increase the risk of adverse effects and toxicity.
To address these challenges, healthcare providers must carefully consider factors such as the child's age, weight, and stage of development when determining the appropriate antibiotic regimen. This may involve adjusting the dosage, frequency, or route of administration to achieve the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing the potential for harm.
Additionally, ongoing monitoring and therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) can be invaluable tools in guiding dosage adjustments and ensuring the safety of antibiotic therapy in pediatric patients. By closely tracking drug concentrations and adjusting the dosage accordingly, healthcare providers can optimize treatment outcomes and minimize the risk of adverse effects.
As we navigate the complex landscape of pediatric antibiotic pharmacokinetics, it is essential to remain vigilant and to continuously seek out the latest evidence-based guidance. By staying informed and employing a patient-centered approach, we can ensure that our youngest patients receive the safe and effective antibiotic treatment they deserve.
What other key considerations do you believe are important when prescribing antibiotics for children? Share your thoughts and insights in the comments below.
User comments
More Topics to Explore
How does renal dysfunction affect antibiotic pharmacokinetics?
Explore how renal dysfunction can impact the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics, including altered drug metabolism and clearance rates. Discuss strategies for dosage adjustment in patients with compromised renal function.
What role does protein binding play in the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics?
Delve into how protein binding affects the distribution and elimination of antibiotics in the body. Discuss the importance of considering protein binding in determining the dosage and efficacy of antibiotics.
How do drug interactions impact the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics?
Investigate the potential interactions between antibiotics and other drugs, examining how these interactions can alter the pharmacokinetic profiles of antibiotics. Share examples of common drug interactions and their effects.
Is there a connection between obesity and altered antibiotic pharmacokinetics?
Analyze how obesity can affect the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination of antibiotics in the body. Discuss the challenges in dosing antibiotics for obese patients and strategies to optimize therapy.
How does age influence antibiotic pharmacokinetics in the elderly population?
Explore how age-related changes in physiology can impact the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics in the elderly. Discuss alterations in drug metabolism, renal function, and distribution in older patients, along with prescribing considerations.
What impact does liver disease have on antibiotic pharmacokinetics?
Examine the effects of liver disease on the metabolism and elimination of antibiotics, leading to altered pharmacokinetic profiles. Discuss challenges in prescribing antibiotics for patients with liver dysfunction and potential dosage adjustments.
How do suboptimal dosing regimens affect antibiotic pharmacokinetics?
Investigate the consequences of suboptimal dosing, such as underdosing or overdosing, on the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics. Explore the implications for treatment efficacy, antimicrobial resistance, and patient safety.
Can genetic factors influence antibiotic pharmacokinetics and response?
Explore how genetic variations can affect the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics, impacting drug metabolism, transport, and efficacy. Discuss the role of pharmacogenomics in personalized antibiotic therapy and its implications for patient care.
How does the route of administration affect antibiotic pharmacokinetics?
Explore the impact of different administration routes, such as oral, intravenous, and intramuscular, on the pharmacokinetic profiles of antibiotics. Discuss factors influencing drug absorption, distribution, and metabolism based on the route of administration.