Herpes Infections and the Impact of Antiviral Therapy
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Apr-12
The recurrent nature of herpes infections has long been a challenge for healthcare providers and patients alike. Herpes simplex virus (HSV), the causative agent of this chronic condition, can lie dormant within the nervous system and reactivate, leading to painful outbreaks. However, the advent of antiviral therapy has offered a glimmer of hope in managing the frequency and severity of these recurrent episodes.
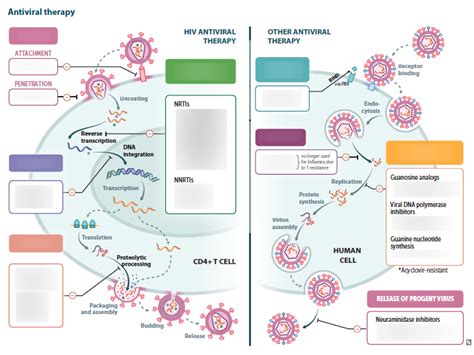
Antiviral medications, such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir, have demonstrated their ability to suppress viral replication and reduce the risk of transmission. When taken as a daily prophylactic treatment or during active outbreaks, these drugs can significantly impact the recurrence rate of herpes infections. Studies have shown that individuals who consistently adhere to antiviral therapy experience a notable decrease in the frequency and duration of their herpes outbreaks, often reporting a reduction of 50% or more in the number of recurrences.
Interestingly, the effectiveness of antiviral therapy can be influenced by a variety of factors, including the type of herpes virus involved (HSV-1 or HSV-2), the individual's immune response, and the timing of treatment initiation. For instance, research suggests that early intervention with antiviral medications, either at the first signs of an outbreak or as a preventive measure, can be more successful in reducing the recurrence rate compared to delayed or intermittent treatment.
Moreover, the route of administration and the specific antiviral drug chosen can also play a role in the treatment outcomes. Oral formulations of antiviral medications have been widely used, providing a convenient and accessible option for patients. However, in certain cases, intravenous administration or the use of topical antiviral creams may be more appropriate, particularly for severe or localized outbreaks.
It's important to note that while antiviral therapy can significantly improve the management of herpes infections, it does not completely eradicate the virus from the body. The herpes virus can still reactivate and cause recurrent outbreaks, even in individuals undergoing consistent treatment. Factors such as stress, hormonal changes, and weakened immune function can all contribute to the reactivation of the virus and the subsequent recurrence of symptoms.
In recent years, researchers have explored the potential of combination therapies, where antiviral medications are used in conjunction with other interventions, such as immunomodulatory agents or therapeutic vaccines. These emerging approaches aim to enhance the long-term control of herpes infections and further reduce the recurrence rate.
As the understanding of herpes infections and the mechanisms of antiviral therapy continues to evolve, healthcare professionals and researchers remain committed to finding more effective ways to manage this chronic condition and improve the quality of life for those affected. By staying informed about the latest advancements in this field, patients can work closely with their healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans that address their individual needs and goals.
So, how does antiviral therapy impact the recurrence rate of herpes infections? The evidence suggests that with the proper use of these medications, individuals can experience a significant reduction in the frequency and severity of their herpes outbreaks, leading to improved overall management of this chronic condition. However, as with any treatment, a comprehensive approach that considers the individual's unique circumstances and ongoing monitoring is essential for optimal outcomes.