The Intricacies of Antiviral Pharmacodynamics: Unraveling the Factors that Shape Therapeutic Outcomes
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Mar-18
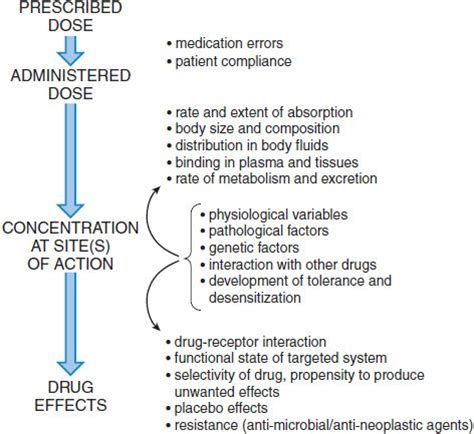
As the world grapples with the ever-evolving landscape of viral infections, the development and optimization of antiviral drugs have become increasingly crucial. However, the effectiveness of these medications can be significantly influenced by a myriad of factors, from drug interactions to patient-specific characteristics. Understanding the key determinants of antiviral pharmacodynamics is essential for healthcare professionals to ensure optimal treatment strategies and patient outcomes.
At the heart of antiviral pharmacodynamics lies the complex interplay between the drug, the target virus, and the host's biological systems. One of the primary factors influencing this dynamic is the drug-drug interactions that can occur when antiviral agents are administered alongside other medications. The metabolism and clearance of antiviral drugs can be altered by concurrent therapies, leading to suboptimal concentrations or even increased toxicity. Healthcare providers must carefully assess potential interactions and monitor patients closely to mitigate these risks.
Equally important is the dosing schedule of antiviral medications. The frequency and timing of administration can significantly impact the drugs' bioavailability, distribution, and ultimately, their ability to effectively target and neutralize the viral infection. Factors such as the drug's half-life, the required therapeutic concentration, and the virus's susceptibility to the medication all play a crucial role in determining the optimal dosing regimen.
Another critical factor influencing antiviral pharmacodynamics is the development of drug resistance. Viruses, with their remarkable capacity for mutation and adaptation, can evolve mechanisms to evade the effects of antiviral drugs. This phenomenon can lead to the emergence of resistant viral strains, rendering the initial treatment less effective or even ineffective. Careful monitoring of viral load and the early detection of resistance patterns are essential to proactively address this challenge and maintain therapeutic efficacy.
Lastly, the patient's individual characteristics can significantly impact the pharmacodynamics of antiviral drugs. Factors such as age, comorbidities, genetic variations, and liver or kidney function can all influence the drug's absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Healthcare providers must consider these patient-specific factors when prescribing antiviral medications, adjusting dosages and monitoring regimens accordingly to ensure optimal therapeutic outcomes.
In the ever-evolving landscape of viral infections, understanding the complex factors that shape antiviral pharmacodynamics is paramount. By recognizing the influence of drug interactions, dosing schedules, resistance development, and patient characteristics, healthcare professionals can navigate the intricacies of antiviral therapy and provide tailored, evidence-based treatments that maximize the effectiveness of these vital medications. As the world continues to grapple with emerging viral threats, this knowledge will be a crucial asset in the ongoing battle to combat and control these formidable infectious agents.