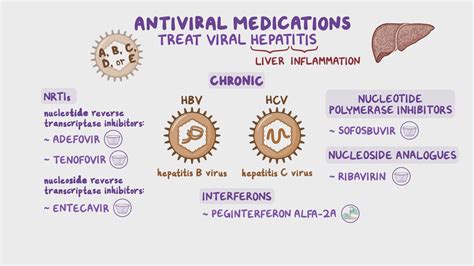
The Treatment Dilemma: Understanding the Risks of Long-Term Antiviral Use for Hepatitis
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Apr-09
Hepatitis, a condition characterized by the inflammation of the liver, can be a chronic and debilitating disease that requires careful management. In many cases, healthcare providers turn to antiviral medications as a primary line of defense, aiming to suppress the virus and prevent further liver damage. However, the long-term use of these antiviral drugs is not without its risks, and patients and their medical teams must weigh the benefits against the potential complications.
Liver Function Impairment
One of the primary concerns with prolonged antiviral therapy is the potential for these medications to adversely impact liver function. While the antivirals are designed to target the hepatitis virus, they can also inadvertently interfere with the liver's natural ability to metabolize and process other substances. This can lead to a build-up of toxins within the body, further exacerbating the already compromised state of the liver.
Drug Resistance and Viral Mutations
Another notable risk associated with long-term antiviral use is the development of drug resistance and viral mutations. Hepatitis viruses, particularly Hepatitis B and C, are known for their ability to rapidly adapt and evolve in response to treatment. Over time, the virus may mutate and become resistant to the prescribed antiviral medication, rendering the treatment ineffective and necessitating a change in the therapeutic approach.
Adverse Side Effects
Antiviral medications, while essential in managing hepatitis, can also produce a range of undesirable side effects. These may include fatigue, nausea, headaches, and even more severe complications, such as anemia or depression. Prolonged exposure to these side effects can significantly impact a patient's quality of life and overall well-being.
Increased Risk of Comorbidities
The long-term use of antiviral medications has also been linked to an increased risk of developing other medical conditions, such as cardiovascular problems, kidney issues, or metabolic disorders. These comorbidities can further complicate the patient's overall health, requiring additional interventions and potentially reducing the efficacy of the hepatitis treatment.
Balancing Risks and Benefits
Navigating the treatment of chronic hepatitis is a delicate balance, and healthcare providers must carefully weigh the risks and benefits of long-term antiviral therapy. In some cases, the potential benefits of suppressing the hepatitis virus and preventing liver damage may outweigh the risks, particularly in more severe or high-risk cases. However, in other instances, healthcare teams may opt for a more conservative approach, utilizing antiviral medications judiciously and closely monitoring patients for any signs of complications.
As with any medical treatment, it is essential for patients to work closely with their healthcare providers to understand the potential risks and make informed decisions about their care. Regular check-ups, laboratory tests, and open communication can help identify and manage any adverse effects or complications that may arise during the course of long-term antiviral therapy.
What are your thoughts on the potential risks associated with the long-term use of antiviral medications for hepatitis? Share your insights and experiences in the comments below.