What role do healthcare professionals play in combatting community-acquired antibiotic resistance?
Analyze the impact and responsibilities of healthcare providers in fighting antibiotic resistance in community-acquired infections.
Healthcare Professionals' Pivotal Role in Combatting Community-Acquired Antibiotic Resistance
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Mar-21
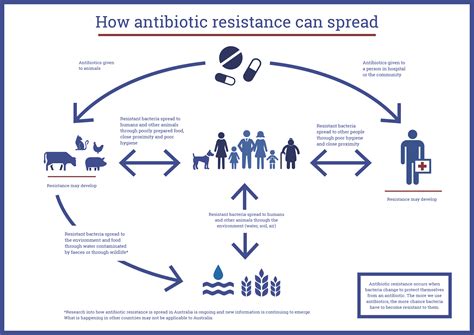
As the issue of antibiotic resistance continues to escalate globally, the role of healthcare professionals in combatting this challenge has become increasingly vital. Community-acquired infections, where pathogens are contracted outside of healthcare settings, present a unique set of concerns when it comes to the spread of antimicrobial resistance.
At the frontlines of this battle are the healthcare providers - physicians, nurses, pharmacists, and other allied health personnel - who are responsible for diagnosing, treating, and educating patients on the appropriate use of antibiotics. Their actions and decisions can have a profound impact on the trajectory of antibiotic resistance within the communities they serve.
One of the primary responsibilities of healthcare professionals is to exercise prudent antimicrobial stewardship. This involves carefully selecting the most appropriate antibiotic, dosage, and duration of treatment for each patient, based on the specific pathogen and the individual's clinical presentation. Overuse or misuse of antibiotics is a key driver of resistance, and healthcare providers must be vigilant in ensuring judicious prescription practices.
Additionally, healthcare professionals play a crucial role in educating patients on the importance of completing the full course of prescribed antibiotics, even if symptoms improve. Incomplete treatment can lead to the development of resistant strains, which can then be transmitted within the community. Empowering patients to understand the risks associated with improper antibiotic use is a critical component of the fight against community-acquired resistance.
Beyond the clinical setting, healthcare providers also have a responsibility to collaborate with public health authorities and policymakers to address the broader systemic factors contributing to antibiotic resistance. This may involve advocating for stricter regulations on antibiotic use in agriculture, supporting the development of new antimicrobial therapies, and promoting awareness campaigns within the community.
Moreover, healthcare professionals can serve as role models and champions for infection prevention and control measures. Proper hand hygiene, effective cleaning and disinfection protocols, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) within healthcare settings can help limit the spread of resistant pathogens and protect both patients and healthcare workers.
In the face of this global challenge, the role of healthcare professionals in combatting community-acquired antibiotic resistance is multifaceted and crucial. By exercising prudent antimicrobial stewardship, educating patients, collaborating with stakeholders, and leading by example, they can make a significant impact on preserving the effectiveness of these vital medicines and safeguarding public health. As the battle against antibiotic resistance continues, the dedication and expertise of healthcare professionals will be instrumental in shaping a future where these life-saving drugs remain a reliable and effective tool in the treatment of infections.
User comments
More Topics to Explore
How can we prevent community-acquired antibiotic resistance?
Discuss strategies for preventing antibiotic resistance in community settings and share effective prevention methods.
Are there specific antibiotics more prone to community-acquired resistance?
Explore the antibiotics that are more susceptible to resistance in community settings and discuss reasons behind this trend.
How does poor sanitation contribute to community-acquired antibiotic resistance?
Examine the relationship between inadequate sanitation practices and the development of antibiotic resistance in community settings.
What are the consequences of untreated community-acquired antibiotic-resistant infections?
Delve into the potential outcomes and risks associated with untreated antibiotic-resistant infections in the community.
Can education and awareness campaigns help reduce community-acquired antibiotic resistance?
Debate the effectiveness of educational initiatives and awareness campaigns in lowering antibiotic resistance rates in community-acquired infections.
Is livestock farming a contributing factor to community-acquired antibiotic resistance?
Investigate the potential influence of livestock farming practices on the development of antibiotic resistance in the community.
What are the challenges in diagnosing community-acquired antibiotic-resistant infections?
Highlight the difficulties and obstacles healthcare professionals face when diagnosing antibiotic-resistant infections in the community.
How can individuals help combat community-acquired antibiotic resistance?
Discuss ways in which individuals can actively contribute to reducing antibiotic resistance in community settings and promoting responsible antibiotic use.
What are the current trends in community-acquired antibiotic resistance?
Explore the latest patterns and developments in antibiotic resistance within community settings and discuss emerging trends.