Antiviral Resistance Surveillance in Influenza: Safeguarding Global Health Through Innovative Monitoring
Posted by Rick Ashworth, reviewed by Dr. Miguel Sanchez | 2024-Apr-04
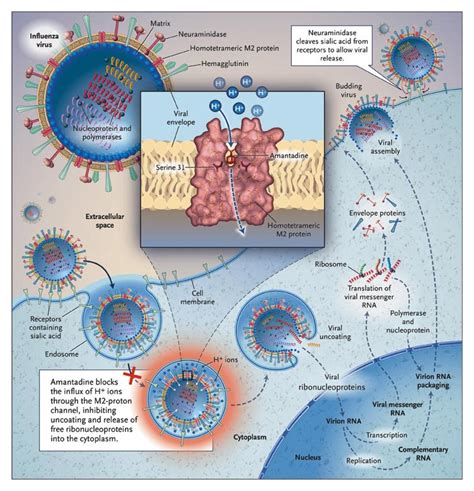
As the world grapples with the ever-evolving influenza virus, the need for robust and comprehensive antiviral resistance surveillance has become increasingly crucial. Influenza, a highly contagious respiratory illness, poses a significant threat to public health, with the potential to cause global pandemics that can disrupt economies and claim countless lives. In this context, the surveillance of antiviral resistance in influenza strains has emerged as a critical component in the ongoing fight against this formidable foe.
Monitoring the emergence and spread of antiviral-resistant influenza strains is essential for ensuring the continued effectiveness of antiviral medications, which play a pivotal role in both the treatment and prophylaxis of influenza. As these viruses evolve, they can develop resistance to commonly used antiviral drugs, rendering them less effective or even entirely ineffective. This phenomenon can have far-reaching consequences, compromising our ability to effectively manage and contain influenza outbreaks, and ultimately jeopardizing global health security.
To address this challenge, public health authorities and research institutions around the world have been at the forefront of developing and implementing best practices in antiviral resistance surveillance. These efforts have focused on enhancing our understanding of the underlying mechanisms of antiviral resistance, improving detection methods, and fostering global collaborations to create a comprehensive, real-time monitoring system.
One of the key innovations in this field is the integration of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies into antiviral resistance surveillance. By leveraging the power of NGS, researchers can now rapidly and accurately identify genetic mutations associated with antiviral resistance in influenza samples, enabling earlier detection and more effective tracking of emerging resistance patterns. This technological advancement has significantly improved the timeliness and precision of antiviral resistance monitoring, allowing public health officials to make more informed decisions and implement targeted interventions.
Moreover, global initiatives, such as the World Health Organization's Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System (GISRS), have been instrumental in coordinating antiviral resistance surveillance efforts on an international scale. These collaborative networks facilitate the sharing of influenza data, including antiviral resistance information, among participating countries, enabling the rapid identification and communication of emerging threats.
As the field of antiviral resistance surveillance continues to evolve, we are also witnessing the emergence of innovative data-driven approaches. The utilization of advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence algorithms has the potential to revolutionize the way we detect, track, and respond to antiviral resistance in influenza. By leveraging these technological advancements, public health authorities can identify patterns, predict trends, and make more informed decisions, ultimately strengthening our ability to combat the threat of antiviral-resistant influenza strains.
In conclusion, the importance of antiviral resistance surveillance in influenza cannot be overstated. As we navigate the ever-changing landscape of this formidable virus, the continued advancement of surveillance strategies, the integration of cutting-edge technologies, and the fostering of global collaborations will be essential in safeguarding our collective health and well-being. By staying vigilant and embracing innovative solutions, we can enhance our readiness and resilience in the face of this enduring public health challenge.